Research - (2021) Volume 9, Issue 10
A Study to Assess the Effectiveness of Structured Teaching Programme Regarding Cancer Therapy among the College Students in a Selected College at Chennai
C Geetha, G Gowri and AR Bharathi*
*Correspondence: AR Bharathi, Department of Nursing, Bharath university, India, Email:
Abstract
Background: Cancer therapy describes the treatment of cancer in a patient, often with surgery. Chemotherapy, radiation therapy, targeted therapy, immunotherapy, hormone therapy are also available for some cancer types. As per Indian Population census data, the rate of mortality due to cancer in India was high and alarming with about 8, 06,000 existing cases by the end of the last century. Objective: “A study to assess the effectiveness of structured teaching programme regarding cancer therapy among the college students in a selected college at Chennai”. Methodology: The selected study design was Quasi-experimental research design (one group pre-test and post-test design). A purposive random sampling technique was used for the study. The sample size for the study consists of 50 students between the age group of 18-23 years. The data collection period was two weeks. Permission was obtained from the Head of the Department of Nursing conducting the study at College of nursing .Self Structured Questionnaires were administered and structured teaching programme on cancer therapy was given who Undergone pre-test. During the slide show session, students asked many doubts and it was clarified. The post test was administered with the same tool to the same group after 7 days. Results: The study finding shows that 50 (100%) had inadequate, none of them had moderate knowledge, none of them had adequate knowledge in pre-test. In post- test 2 (4%) had inadequate knowledge, 21 (42%) had moderate knowledge and 27 (54%) had adequate knowledge. The study findings revealed that there was a significant improvement in the post test. The improvement mean score was in pre-test 22% and in post-test 77.68% with ‘t’ value 23.2 which shows high significant at p<0.05, it shows the effectiveness of structure teaching programme. Conclusion: The study concluded that structured teaching programme was effective in improving knowledge towards cancer therapy.
Keywords
Cancer therapy, Structured teaching programme, Student
Introduction
“Time is shortening, but every day that we challenge this cancer and survive is a victory for us "-Ingrid Bergman. The goal of treatment is to achieve a cure for the cancer, allowing man to live a normal life span. This may or may not be possible, depending on their specific situation [1]. Cancer therapy describes the treatment of cancer in a patient, often with surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, targeted therapy, immunotherapy, hormone therapy are also available for some cancer types. In worldwide incidence, there were 17 million new cases of cancer in 2018. Cancer is a second leading cause of death globally, and is responsible for an estimated death in 2018. Globally, about 1 in 6 deaths due to cancer. Tobacco use is the most important risk factor for cancer and is responsible for approximately 22% of cancer deaths. The three most common cancers occurring worldwide are lung cancer, breast cancer for females and colorectal cancer - contributed 44.4% of all cancers. Worldwide there will be 27.5 million new cases of cancer each year by 2040 [2].
As per Indian Population census data, the rate of mortality due to cancer in India was high and alarming with about 8, 06,000 existing cases by the end of the last century. Cancer statistics in Tamil Nadu, the annual cancer burden predicted for 2012 - 2016 is 6,100 for Chennai, translating to 55,000 new cases per year in state-wide (in Tamil Nadu) [2].
Methodology
The selected study design was Quasi-experimental research design (one group pre-test and post-test design). A purposive random sampling technique was used for the study. The sample size for the study consists of 50 students between the age group of 18-23 years. The data collection period was two weeks. Permission was obtained from the principal for conducting the study at Meenakshi College of nursing .Self structured questionnaires were administered and Structured teaching programme on cancer therapy was given who Undergone pre-test. During the slide show session, students asked many doubts and it was clarified. The post test was administered with the same tool to the same group after 7 days.
Results
Results are mentioned in the Tables and Figures (Tables 1 to Table 4), (Figures 1 to Figure 2).
Table 1: Analysis of demographic data of the student in IV years B.SC (Nursing).
| S.NO | Categories | Demographic variables | Frequency (n) | Percentage (% ) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Age | 8-19years | 1 | 2% |
| 20-21years | 44 | 88% | ||
| 22-23years | 5 | 10% | ||
| 2 | Sex | Male | 7 | 14% |
| Female | 43 | 86% | ||
| 3 | Religion | Hindu | 39 | 78% |
| Christian | 9 | 18% | ||
| Muslim | 2 | 4% | ||
| Others | 0 | 0% | ||
| 4 | Socio Economic Status | Low | 1 | 2% |
| Middle | 48 | 96% | ||
| High | 1 | 2% | ||
| 5 | food pattern | Vegetarian | 7 | 14% |
| Non vegetarian | 43 | 86% | ||
| 6 | Type of Family | Joint | 8 | 16% |
| Nuclear | 42 | 98% | ||
| 7 | Source of Information | News paper | 9 | 18% |
| Television and internet | 35 | 70% | ||
| Close relative | 2 | 4% | ||
| Other source | 4 | 8% |
Table 2: Frequency and percentage distribution in pre-test and post-test.
| S. No | Level of knowledge | Pre-test | Post-test | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | % | N | % | ||
| 1 | Inadequate knowledge | 5 | 100 | 2 | 4 |
| 2 | Moderate knowledge | 0 | 0 | 21 | 42 |
| 3 | Adequate knowledge | 0 | 0 | 27 | 54 |
Table 3: Comparison of mean and standard deviation of pre-test and post-test to assess the knowledge level.
| Sl. no. | Subjects | Mean | Standard deviation | 'T' Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Pre-test | 22 | 1.75 | 23.2 |
| 2 | Post-test | 77.68 | 3.65 |
Table 4: Association of knowledge with all the demographic variables.
| S. No. | Categories | Demographic variables | Frequency | Chi-Square |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Age | 18-19 years | 1 | 4.5826 |
| 20-21 years | 44 | NS at 0.05% level | ||
| 22-23years | 5 | |||
| 2 | Sex | Male | 7 | 0.4569 |
| Female | 43 | NS at 0.05% level | ||
| 3 | Religion | Hindu | 39 | 11.3658 |
| Christian | 9 | NS at0.05%level | ||
| Muslim | 2 | |||
| Others | 0 | |||
| 4 | Socio-economic status | Low | 1 | 2.877 |
| Middle | 48 | NS at0.05%level | ||
| High | 1 | |||
| 5 | Food pattern | Vegetarian | 7 | 2.5171 |
| Non-vegetarian | 43 | NS at0.05%level | ||
| 6 | Type of family | Joined family | 8 | 1.814 |
| Nuclear family | 42 | NS at0.05%level | ||
| 7 | Type of family | News paper | 9 | 230.7988 |
| Television and internet | 35 | Significant at0.05%level | ||
| Close relative | 2 | |||
| Other source | 4 |
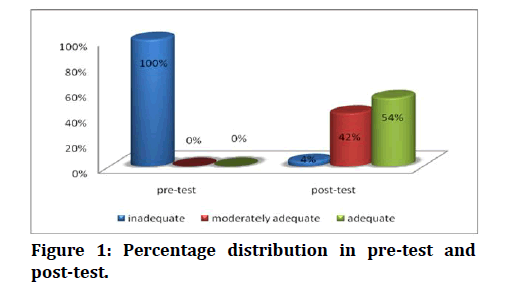
Figure 1: Percentage distribution in pre-test and post-test.
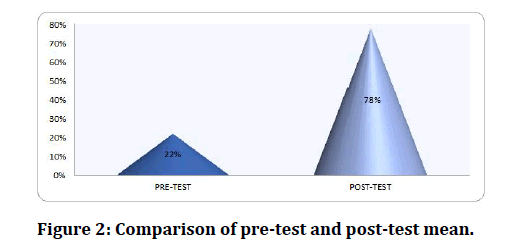
Figure 2: Comparison of pre-test and post-test mean.
Discussion
Dagogo-Jack, et al. [3] conducted a study to assess the effectiveness structured teaching programme regarding cancer therapy. The Women in knowledge regarding breast cancer and breast self-examination (BSE).The study was designed the effectiveness of teaching programme to enhance knowledge and assess the skill of BSE among mahilamandal women Quasi experimental (one group pre-test and post-test design). The pre-test knowledge was assessed using structured interview schedule and BSE skill was assessed by observation check list out of 42 women. The mean pre-test knowledge score (7.6 ± 3.0) was less than post-test knowledge score (24.9 ± 2.7). The mean pre-test skill score (0.7 ± 1.0) was also less than post-test skill score (12.4 ± 2.0). The paired t value between the pre-test and post-test knowledge and skill score statistically significant at 0.001 levels. Conclusion of the study structured teaching programme was an effective strategy in improving the knowledge and skill of women regarding breast cancer and BSE.
The findings of the present study revealed that, there was no significant association between on demographic variables such as age, gender, religion, socio-economic status, food pattern, type of family, information got through. There was significant association at P<0.05 level. It is possible that they are exposed to more through newspaper, television and internet, close relative, other source [4-29].
Conclusion
The pre-test knowledge had an overall score of 22% and post-test knowledge had an overall score of 77.68%. The improvement meaning score of post-test was 19.42 with t value (t=23.2). There was significant difference in the level of knowledge, highly significant at P<0.05 shows the effectiveness of structured teaching programme. The findings of the study demonstrated that on education session increase the knowledge and compliance.
Funding
No funding sources.
Ethical Approval
The study was approved by the Institutional Ethics Committee.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Acknowledgment
The encouragement and support from Bharath Institute of Higher Education and Research, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India is gratefully acknowledged for providing the laboratory facilities to carry out the research work.
References
- Bonadonna G, Valagussa P. Dose-response effect of adjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer. New England J Med 1981; 304:10-15.
- American Cancer Society. Cancer facts & figures 2015. American Cancer Society; 2015. Int J Community medicine Public Health 2016; 3:2940.
- Dagogo-Jack I, Shaw AT. Tumour heterogeneity and resistance to cancer therapies. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 2018; 15:81â??94.
- Martinelli C, Pucci C, Ciofani G. Nanostructured carriers as innovative tools for cancer diagnosis and therapy. APL Bioeng 2019; 3:011502.
- Kumar B, Garcia M, Murakami JL, et al. Exosome-mediated microenvironment dysregulation in leukemia. Biochim Biophys Acta 2016; 1863:464â??470.
- Chikara S, Nagaprashantha LD, Singhal J, et al. Oxidative stress and dietary phytochemicals: role in cancer chemoprevention and treatment. Cancer Lett 2018; 413:122â??134.
- Singh S, Sharma B, Kanwar SS, et al. Lead phytochemicals for anticancer drug development. Front Plant Sci. 2016; 7:1667.
- Bazak R, Houri M, El Achy S, et al. Cancer active targeting by nanoparticles: a comprehensive review of literature. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 2015; 141:769â??784.
- Lebedeva IV, Su ZZ, Sarkar D, et al. Restoring apoptosis as a strategy for cancer gene therapy: focus on p53 and mda-7. Semin Cancer Biol 2003; 13:169â??178.
- Shanker M, Jin J, Branch CD, et al. Tumor suppressor gene-based nanotherapy: from test tube to the clinic. J Drug Deliv 2011; 465845.
- Vaishnaw AK, Gollob J, Gamba-Vitalo C, et al. A status report on RNAi therapeutics. Silence 2010; 1:14.
- Brace C. Thermal tumor ablation in clinical use. IEEE Pulse. 2011; 2:28â??38.
- Hervault A, Thanh NTK. Magnetic nanoparticle-based therapeutic agents for thermo-chemotherapy treatment of cancer. Nanoscale 2014; 6:11553â??11573.
- Yu KH, Zhang C, Berry GJ, et al. Predicting non-small cell lung cancer prognosis by fully automated microscopic pathology image features. Nat Commun 2016; 7:12474.
- Aerts HJWL. The potential of radiomic-based phenotyping in precision medicine a review. JAMA Oncol 2016; 2:1636â??1642.
- Grove O, Berglund AE, Schabath MB, et al. Quantitative computed tomographic descriptors associate tumor shape complexity and intratumor heterogeneity with prognosis in lung adenocarcinoma. PLoS One 2015; 10:e0118261.
- Aerts HJWL, Velazquez ER, Leijenaar RTH, et al. Decoding tumour phenotype by noninvasive imaging using a quantitative radiomics approach. Nat Commun 2014; 5:4006.
- Kong J, Cooper LAD, Wang F, et al. Machine-based morphologic analysis of glioblastoma using whole-slide pathology images uncovers clinically relevant molecular correlates. PLoS One 2013; 8:e81049.
- Tinkle S, Mcneil SE, Mühlebach S, et al. Nanomedicines: Addressing the scientific and regulatory gap. Ann N Y Acad Sci 2014; 1313:35â??56.
- Albanese A, Tang PS, Chan WCW. The effect of nanoparticle size, shape, and surface chemistry on biological systems. Annu Rev Biomed Eng 2012; 14:1â??16.
- Maeda H. Toward a full understanding of the EPR effect in primary and metastatic tumors as well as issues related to its heterogeneity. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 2015; 91:3â??6.
- Gerlowski LE, Jain RK. Microvascular permeability of normal and neoplastic tissues. Microvasc Res 1986; 31:288â??305.
- Shi J, Kantoff PW, Wooster R, et al. Cancer nanomedicine: progress, challenges and opportunities. Nat Rev Cancer 2017; 17:20â??37.
- Shi J, Votruba AR, Farokhzad OC, et al. Nanotechnology in drug delivery and tissue engineering: From discovery to applications. Nano Lett 2010; 10:3223â??3230.
- Sinha R. Nanotechnology in cancer therapeutics: Bioconjugated nanoparticles for drug delivery. Mol Cancer Ther 2006; 5:1909â??1917.
- Bregoli L, Movia D, Gavigan-Imedio JD, et al. Nanomedicine applied to translational oncology: A future perspective on cancer treatment. Nanomed 2016; 12:81â??103.
- Kim EM, Jeong HJ. Current status and future direction of nanomedicine: Focus on advanced biological and medical applications. Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2017; 51:106â??117.
- Martinelli C. Exosomes: New biomarkers for targeted cancer therapy. In Molecular oncology: Underlying mechanisms and translational advancements 2017; 129-157.
- Siravegna G, Marsoni S, Siena S, et al. Integrating liquid biopsies into the management of cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 2017; 14:531â??548.
Author Info
C Geetha, G Gowri and AR Bharathi*
Department of Nursing, Bharath university, Chennai, IndiaCitation: C Geetha, G Gowri, AR Bharathi,A Study to Assess the Effectiveness of Structured Teaching Programme Regarding Cancer Therapy among the College Students in a Selected College at Chennai, J Res Med Dent Sci, 2021, 9(10): 127-131
Received: 17-Sep-2021 Accepted: 30-Sep-2021
