Research - (2021) Volume 9, Issue 10
Antioxidant Activity of Silver Nanoparticles Synthesized Using Vetiveria zizanioides-In Vitro Study
Shifa Jawahar Ali1, Abirami Arthanari1* and S Rajeshkumar2
*Correspondence: Abirami Arthanari, Department of Forensic Odontology Saveetha Institute of Medical and Technical Sciences (SIMATS), Saveetha University, India, Email:
Abstract
Introduction: Nanotechnology has a wide range of biomedical applications and nanoparticles can be devised to possess unique composition and functionalities, which can provide novel tools and techniques in biomedical research. Nanotechnology is one of the rapidly developing sciences in the past few years. Nanoparticles are materials that have all their dimensions in the Nano scale and measured in nanometres. The size-dependent physicochemical properties of nanoparticles promote their application in many products but the same unique properties also can lead to physiological responses in living systems by interaction with these materials. Aim: The aim of the present study is to synthesize silver nanoparticles from aqueous extract of Vetiveria zizanioides plant and to evaluate its antioxidant potential. Materials and methods: Plant extract of Vetiveria zizanioides was prepared and filtered by Whatman No 1 filter paper. Silver nitrate was added to the plant extract and kept in a magnetic stirrer for nanoparticle synthesis. The synthesized nanoparticle was preliminarily analysed using UV visible spectroscopy. Finally the left over solution was taken to calculate antioxidant activity. Results and discussion: Antioxidant activity was calculated by DPPH method and the percentage of inhibition of silver nanoparticles synthesised from Vetiveria zizanioides was 46.9% for 10µL, 56.9% for 20µL, 61.5% for 30µL, 67.3% for 40µL and 72.4% for 50µL. Hence maximum inhibition was observed at 50µL that is at higher concentration Conclusion: We can conclude that silver nanoparticles synthesised from Vetiveria zizanioides are a potent antioxidant agent. Since it shows a good activity in free radical scavenging, silver nanoparticles can be used in a clinical therapeutic application.
Keywords
Antioxidant activity, Silver nanoparticles, Vetiveria zizanioides, DPPH assay, Innovative technique, Green synthesis
Introduction
Nanotechnology has a wide range of biomedical applications and nanoparticles can be devised to possess unique composition and functionalities, which can provide novel tools and techniques in biomedical research [1]. In recent years, nanotechnology has been one of the most rapidly developing fields, with more studies reported on it [2-4]. Nanoparticles are materials that have all their dimensions in the Nano scale and measured in nanometres [5]. Nanoparticles can be used in medicine due to its increased interaction with microbes and has less side effects than drugs by reducing damage to healthy cells. The size-dependent physicochemical properties of nanoparticles promote their application in many products but the same unique properties also can lead to physiological responses in living systems by interaction with these materials [6]. Due to its superior physical, chemical, and biological properties, silver nanoparticles have recently gained a lot of attention [7]. Their superiority derives primarily from the scale, shape, composition, crystallinity, and arrangement of silver nanoparticles relative to their bulk types [8]. Efforts are being made to explore their attractive properties and utilize them in practical applications, such as anti-bacterial and anti-cancer therapeutics [9-12], diagnostics and optoelectronics [13], water disinfection [14], and other clinical/pharmaceutical applications [15].
Vetiveria zizanioides is an evergreen, perennial herb, having an appearance similar to lemongrass is found throughout the plains and lower hills of India, particularly on the riverbanks and in rich marshy soil [16]. Vetiveria zizanioides can prevent soil erosion and is also helpful in rehabilitating metal-polluted soil [17]. Traditionally, the plant is used for aromatherapy, for stress, anxiety, nervous tension and insomnia [18]. Vetiveria zizanioides has been cultivated for many industrial applications, including the production of the commercially and medicinally valued volatile oil that can be obtained from its root [19]. Vetiver oil is commonly used as a odour contributor in the perfumery industry, cosmetics, soaps and used as a flavour agent in the food industry [20]. The essential oil of its root also appears to possess antioxidant activity [21].
One of the main contributing factors in the pathogenesis of many chronic disorders is oxidative stress [22]. Oxidative stress is a condition that happens when the balance between a cell's antioxidative defence and oxidants is disturbed by the presence of excessive oxidants. Free radicals and other reactive oxygen species are important factors in the ageing process [23]. As a result of the mitochondria's production of ATP, free radicals are generated when cells use oxygen to generate energy. Antioxidants fundamentally inhibit free radical propagation in biological systems [24,25]. The antioxidant capacity can be measured in medicinal plants or other materials for characterisation of the property [26-28]. Antioxidant activity of silver nanoparticles synthesised from aqueous extract of Vetiveria zizanioides plant has not yet been investigated. Our team has extensive knowledge and research experience that has translated into high quality publications [29-49]. The aim of the present study is to synthesize silver nanoparticles from aqueous extract of Vetiveria zizanioides plant and to evaluate its antioxidant potential.
Material and Method
Extract preparation
In the present study, 1gm of Vetiveria zizanioides was added in 100 ml of distilled water and boiled for 10-15 minutes at 70 degree Celsius. After boiling, the plant extract was filtered by Whatman No 1 filter paper. 60 ml of 20 milli molar silver nitrate was prepared in 250 ml of conical flask; 40 ml of filtered plant extract was mixed to it and kept in a magnetic stirrer for nanoparticle synthesis. Colour change was observed after nanoparticle synthesis (figure 1&2). The synthesized nanoparticle was preliminarily analysed using UV visible spectroscopy. Prior to the final step, the nanoparticle solution was centrifuged at 8000 rpm to prepare nanoparticle pellet powder; it was dried in a hot air oven at 80 degree Celsius. The dried powder was sent for characterisation. Finally the left over solution was taken to evaluate its antioxidant activity. All the results were taken photographs and recorded in the excel sheets.
Figure 1. Figure represents the colour change observed after nanoparticle synthesis.
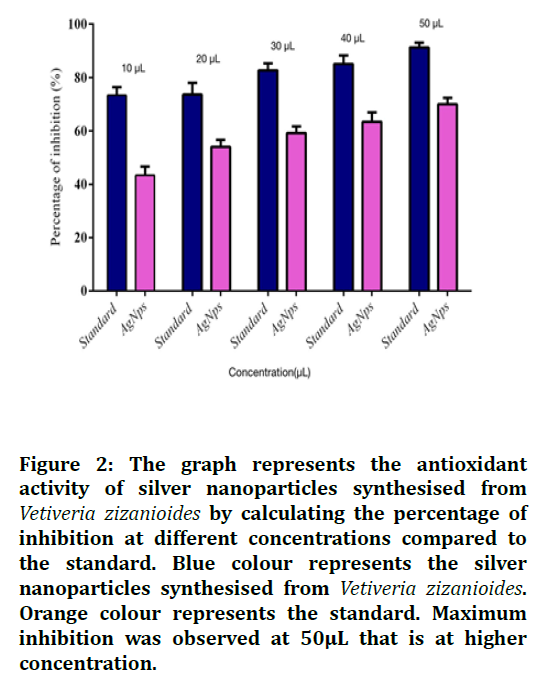
Figure 2. The graph represents the antioxidant activity of silver nanoparticles synthesised from Vetiveria zizanioides by calculating the percentage of inhibition at different concentrations compared to the standard. Blue colour represents the silver nanoparticles synthesised from Vetiveria zizanioides. Orange colour represents the standard. Maximum inhibition was observed at 50μL that is at higher concentration.
Antioxidant assay-DPPH method
DPPH assay was used to test the antioxidant activity of biogenic synthesized silver nanoparticles. Diverse concentrations (2-10 μg/ml) of Vetiveria zizanioides plant extract interceded silver nanoparticles were mixed with 1 ml of 0.1 mm DPPH in methanol and 450 μl of 50 mm Tris HCl buffer (pH 7.4) and incubated for 30 minutes. Later, the reduction in the quantity of DPPH free radicals was assessed dependent on the absorbance at 517 nm. BHT was employed as control. The percentage of inhibition was determined from the following equation,
% inhibition=Absorbance of control- Absorbance of test sample X 100/Absorbance of control
Results
The percentage of inhibition of silver nanoparticles synthesised from Vetiveria zizanioides was 46.9% for 10μL, 56.9% for 20μL, 61.5% for 30μL, 67.3% for 40μL and 72.4% for 50μL. The percentage of inhibition of the standard was 76.56% for 10μL, 78.52% for 20μL, 85.63% for 30μL, 88.68% for 40μL and 93.15% for 50μL. Hence maximum inhibition was observed at 50μL that is at higher concentration (Table 1)(Figure 2). The silver nanoparticles synthesised from Vetiveria zizanioides have good antioxidant activity and are comparable to the standard.
| No. | Concentration | Standard- % of Inhibition | Silver nanoparticles-% of Inhibition |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 10µL | 76.56 | 46.9 |
| 2 | 20µL | 78.52 | 56.9 |
| 3 | 30µL | 85.63 | 61.5 |
| 4 | 40µL | 88.68 | 67.3 |
| 5 | 50µL | 93.15 | 72.4 |
Table 1: The table represents the antioxidant activity of silver nanoparticles synthesised from Vetiveria zizanioides compared to the standard.
Discussion
Previous research works have reported on the various activities exhibited by the nanoparticles synthesised from natural sources such as cytotoxic and antimicrobial activity [50-52]. In a study, silver nanoparticles were synthesized from aqueous leaf extract of Cestrum nocturnum and its antioxidant and antibacterial activities were tested. The bacteriostatic and bactericidal activity of silver nanoparticles against 3 bacteria Escherichia coli, Enterococcus faecalis, and Salmonella typhi was determined using bacterial growth inhibition method. The results confirmed that the silver nanoparticles have more antioxidant activity as compared to vitamin C. Antioxidant and antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles is due to the presence of bioactive molecules on the surface.
Silver nanoparticles were synthesised in a study, using an aqueous extract of the Nepeta deflersiana plant. Human cervical cancer cells were used to test the anticancer activity of silver nanoparticles synthesised from Nepeta deflersiana. The cytotoxic reaction was found to be concentration dependent. According to the results, there was also a substantial rise in ROS and lipid peroxidation, as well as a decline in MMP and glutathione levels. Biosynthesised silver nanoparticles caused cell death in HeLa cells, implying that silver nanoparticles have anticancer capacity. As a result, they can be used to treat the cervical cancer cells [53].
In future, silver nanoparticles biosynthesised from Vetiveria zizanioides can be assessed for its anticancer, anti-inflammatory, antifungal and antibacterial activity. The study’s limitation was that it was conducted in vitro, so it cannot be assumed that the results of antioxidant activity could be translated into clinical effectiveness.
Conclusion
The silver nanoparticles biosynthesised from Vetiveria zizanioides have good antioxidant activity. We can conclude that silver nanoparticles are a potent antioxidant agent. Since it shows a good activity in free radical scavenging, further studies can be done on silver nanoparticles of its clinical therapeutic application.
Conflict of Interest
The author declares that there is no conflict of interest in the present study.
Acknowledgment
This research was done under the supervision of the Department of research of Saveetha dental college and hospital.
We sincerely show gratitude to the corresponding guide for providing insights and expertise that greatly assisted the research.
Funding Source
The present study was supported by the following agencies.
• Saveetha Dental College SIMATS, Saveetha University.
• Ateeq Al Dhahery Trading Est.
References
- Wang EC, Wang AZ. Nanoparticles and their applications in cell and molecular biology. Integrative Biol 2014; 6:9-26.
- Rajeshkumar S, Malarkodi C, Al Farraj DA, et al. Employing sulphated polysaccharide (fucoidan) as medium for gold nanoparticles preparation and its anticancer study against HepG2 cell lines.Mater. Today Commun 2021; 26:101975.
- Ali SJ, Preetha S, Jeevitha M, et al. Antifungal activity of selenium nanoparticles extracted from capparis decidua fruit against Candida albicans. J Evol Med Dent Sci 2020; 9:2452-456.
- Ganapathy D. Nanobiotechnology in combating CoVid-19. Bioinformation 2020; 16:828–830.
- Murthy SK. Nanoparticles in modern medicine: State of the art and future challenges. Int J Nanomed 2007; 2:129–141.
- Gupta R, Xie H. Nanoparticles in daily life: Applications, toxicity and regulations. J Environ Pathol Toxicol Oncol 2018; 37:209–230.
- Lee SH, Jun BH. Silver nanoparticles: synthesis and application for nanomedicine. Int J Mol Sci 2019; 20:865.
- Syafiuddin A, Salmiati, Salim MR. et al. A review of silver nanoparticles: Research trends, global consumption, synthesis, properties, and future challenges: A review of silver nanoparticles. J Chin Chem Soc 2017; 64:732–756.
- Shathviha PC, Ezhilarasan D, Rajeshkumar S, et al. β-sitosterol mediated silver nanoparticles induce cytotoxicity in human colon cancer HT-29 cells. Avicenna J Med Biotechnol 2021; 13:42–46.
- Nasim I, Kumar SR, Vishnupriya V, et al. Cytotoxicity and anti-microbial analysis of silver and graphene oxide bio nanoparticles. Bioinformation 2020; 16:831-836.
- Jackson K. Cytotoxic potentials of silibinin assisted silver nanoparticles on human colorectal HT-29 cancer cells. Bioinformation 2020; 16:817–827.
- Sreenivasagan S, Subramanian AK, Rajeshkumar S. Assessment of antimicrobial activity and cytotoxic effect of green mediated silver nanoparticles and its coating onto mini-implants. Annals of Phytomed 2020; 9:207–212.
- Chen D, Qiao X, Qiu X, et al. Synthesis and electrical properties of uniform silver nanoparticles for electronic applications. J Mater Sci 2009; 44:1076–1081.
- Dankovich TA, Gray DG. Bactericidal paper impregnated with silver nanoparticles for point-of-use water treatment. Environ Sci Technol 2011; 45:1992–1998.
- Zhang XF, Zhi-Guo liu, Wei Shen, et al. Silver nanoparticles: Synthesis, characterization, properties, applications, and therapeutic approaches. Int J Mol Sci 2016; 17:1534.
- Rao RR, Suseela MR. Vetiveria zizanioides (Linn.) Nash–a multipurpose eco-friendly grass of India. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Vetiver Conference 2000 .
- Chou ST, Shih Y, Lin CC. Vetiver grass (Vetiveria zizanioides) oils. In: Preedy VR. Essential oils in food preservation, flavor and safety. San Diego: Academic Press 2016; 843–848.
- Varadharajan S, Kuppusamy A, Muthuswamy U, et al. In vitro antioxidant activity of Vetiveria zizanioides root extract. Tanzan J Health Res 2010; 12:265–271.
- Peng HY, Lai CC, Lin CC, et al. Effect of Vetiveria zizanioides essential oil on melanogenesis in melanoma cells: downregulation of tyrosinase expression and suppression of oxidative stress. Sci World J 2014; 2014:213013.
- David A, Wang F, Sun X, et al. Chemical composition, antioxidant, and antimicrobial activities of Vetiveria zizanioides (L.) nash essential oil extracted by carbon dioxide expanded ethanol. Molecules 2019; 24:1897.
- Luqman S, Kumar R, Kaushik S, et al. Antioxidant potential of the root of Vetiveria zizanioides (L.) Nash. Indian J Biochem Biophys 2009; 46:122–125.
- Raj RK. β‐Sitosterol‐assisted silver nanoparticles activates Nrf2 and triggers mitochondrial apoptosis via oxidative stress in human hepatocellular cancer cell line. J Biomed Materials Res 2020; 108:1899-1908.
- Shifa J, Gayathri R, Priya VV. Preliminary phytochemical analysis and total phenol content of aqueous fruit extract of Sambucus nigra. Drug Invent Today 2020 ; 13.
- Shunmugam R, Renukadevi Balusamy S, Kumar V, et al. Biosynthesis of gold nanoparticles using marine microbe (Vibrio alginolyticus) and its anticancer and antioxidant analysis. J King Saud Univ Sci 2021; 33:101260.
- Mohapatra S, Leelavathi L, Rajeshkumar S, et al. Assessment of cytotoxicity, anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activity of zinc oxide nanoparticles synthesized using clove and cinnamon formulation--an in-vitro study. J Evol Med Dent Sci 2020; 9:1859.
- Kim H-J, Chen F, Wang X, et al. Evaluation of antioxidant activity of vetiver (Vetiveria zizanioides L.) oil and identification of its antioxidant constituents. J Agric Food Chem 2005; 53:7691–7695.
- Wu S, Rajeshkumar S, Madasamy M, et al. Green synthesis of copper nanoparticles using Cissus vitiginea and its antioxidant and antibacterial activity against urinary tract infection pathogens. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol 2020; 48:1153–1158.
- Rajakumari R, Volova T, Oluwafemi OS, et al. Grape seed extract-soluplus dispersion and its antioxidant activity. Drug Dev Ind Pharm 2020; 46:1219–1229.
- Princeton B, Santhakumar P, Prathap L. Awareness on preventive measures taken by health care professionals attending COVID-19 patients among dental students. Eur J Dent 2020; 14:S105–S109.
- Mathew MG, Samuel SR, Soni AJ, et al. Evaluation of adhesion of Streptococcus mutans, plaque accumulation on zirconia and stainless steel crowns, and surrounding gingival inflammation in primary molars: Randomized controlled trial. Clin Oral Investig 2020; 24:3275–3280.
- Sridharan G, Ramani P, Patankar S, et al. Evaluation of salivary metabolomics in oral leukoplakia and oral squamous cell carcinoma. J Oral Pathol Med 2019; 48:299–306.
- Hannah R, Ramani P, Ramanathan A, et al. CYP2 C9 polymorphism among patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma and its role in altering the metabolism of benzo [a] pyrene. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol 2020; 130:306-312.
- Antony JVM, Ramani P, Ramasubramanian A, et al. Particle size penetration rate and effects of smoke and smokeless tobacco products-An invitro analysis. Heliyon 2021; 7:e06455.
- Sarode SC, Gondivkar S, Sarode GS, et al. Hybrid oral potentially malignant disorder: A neglected fact in oral submucous fibrosis. Oral Oncol 2021; 105390.
- Hannah R, Ramani P, Tilakaratne WM, et al. Critical appraisal of different triggering pathways for the pathobiology of pemphigus vulgaris-A review. Oral Diseas 2021.
- Chandrasekar R, Chandrasekhar S, Sundari KKS, et al. Development and validation of a formula for objective assessment of cervical vertebral bone age. Prog Orthod 2020; 21:38.
- Subramanyam D, Gurunathan D, Gaayathri R, et al. Comparative evaluation of salivary malondialdehyde levels as a marker of lipid peroxidation in early childhood caries. Eur J Dent 2018; 12:67–70.
- Jeevanandan G, Thomas E. Volumetric analysis of hand, reciprocating and rotary instrumentation techniques in primary molars using spiral computed tomography: An in vitro comparative study. Eur J Dent 2018; 12:21–26.
- Ponnulakshmi R, Shyamaladevi B, Vijayalakshmi P, et al. In silico and in vivo analysis to identify the antidiabetic activity of beta sitosterol in adipose tissue of high fat diet and sucrose induced type-2 diabetic experimental rats. Toxicol Mech Methods 2019; 29:276–90.
- Sundaram R, Nandhakumar E, Haseena Banu H. Hesperidin, a citrus flavonoid ameliorates hyperglycemia by regulating key enzymes of carbohydrate metabolism in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Toxicol Mech Methods 2019; 29:644–653.
- Alsawalha M, Rao CV, Al-Subaie AM, et al. Novel mathematical modelling of Saudi Arabian natural diatomite clay. Mater Res Express 2019; 6:105531.
- Yu J, Li M, Zhan D, et al. Inhibitory effects of triterpenoid betulin on inflammatory mediators inducible nitric oxide synthase, cyclooxygenase-2, tumor necrosis factor-alpha, interleukin-6, and proliferating cell nuclear antigen in 1, 2-dimethylhydrazine-induced rat colon carcinogenesis. Pharmacogn Mag 2020; 16:836.
- Shree KH, Ramani P, Sherlin H, et al. Saliva as a diagnostic tool in oral squamous cell carcinoma–a systematic review with meta analysis. Pathol Oncol Res 2019; 25:447-453.
- Zafar A, Sherlin HJ, Jayaraj G, et al. Diagnostic utility of touch imprint cytology for intraoperative assessment of surgical margins and sentinel lymph nodes in oral squamous cell carcinoma patients using four different cytological stains. Diagn Cytopathol 2020; 48:101–10.
- Karunagaran M, Murali P, Palaniappan V, et al. Expression and distribution pattern of podoplanin in oral submucous fibrosis with varying degrees of dysplasia–an immunohistochemical study. J Histotechnol 2019; 42:80-86.
- Sarode SC, Gondivkar S, Gadbail A, et al. Oral submucous fibrosis and heterogeneity in outcome measures: A critical viewpoint. Future Oncol 2021; 17:2123–2126.
- Raj Preeth D, Saravanan S, Shairam M, et al. Bioactive Zinc(II) complex incorporated PCL/gelatin electrospun nanofiber enhanced bone tissue regeneration. Eur J Pharm Sci 2021; 160:105768.
- Prithiviraj N, Yang GE, Thangavelu L, et al. Anticancer compounds from starfish regenerating tissues and their antioxidant properties on human oral epidermoid carcinoma KB cells. In: Pancreas. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Two Commerce SQ 2020; 155–6.
- http://bbrc.in/bbrc/wp-content/uploads/2020/10/13-NO-71-Special-Issue-014.pdf
- Chellapa LR, Shanmugam R, Indiran MA, et al. Biogenic nanoselenium synthesis, its antimicrobial, antioxidant activity and toxicity. Bioinspired Biomim Nanobiomaterials 2020; 9:184–189.
- Menon S, Agarwal H, Rajeshkumar S, et al. Investigating the antimicrobial activities of the biosynthesized selenium nanoparticles and its statistical analysis. Bionanosci 2020; 10:122–135.
- Saravanakumar K, Chelliah R, MubarakAli D, et al. Unveiling the potentials of biocompatible silver nanoparticles on human lung carcinoma A549 cells and Helicobacter pylori. Sci Rep 2019; 9:1-8.
- Al-Sheddi ES, Farshori NN, Al-Oqail MM, et al. Anticancer potential of green synthesized silver nanoparticles using extract of Nepeta deflersiana against human cervical cancer cells (HeLA). Bioinorg Chemi App 2018; 2018.
Author Info
Shifa Jawahar Ali1, Abirami Arthanari1* and S Rajeshkumar2
1Department of Forensic Odontology Saveetha Institute of Medical and Technical Sciences (SIMATS), Saveetha University, Chennai, Tamil Nadu-77, India2Department of Pharmacology, Saveetha Institute of Medical and Technical Sciences (SIMATS), Saveetha University, Chennai, Tamil Nadu-77, India
Citation: Shifa Jawahar Ali, Abirami Arthanari, S Rajeshkumar,Antioxidant Activity of Silver Nanoparticles Synthesized Using Vetiveria zizanioides-In Vitro Study , J Res Med Dent Sci, 2021, 9(10): 199-203
Received: 09-Sep-2021 Accepted: 12-Oct-0021
