Research - (2022) Volume 10, Issue 12
Effect Of Music on Weight Gain in Pre-Term Baby
Mitali Agrawal1*, Bhavana Lakhkar1 and Mahaveer Lakhra2
*Correspondence: Mitali Agrawal, Department of Pediatrics, Jawaharlal Nehru Medical College, Datta Meghe Institute of Medical Sciences, India, Email:
Abstract
When babies are born preterm or suffer from some illness, they need to get admitted in NICU which can lead to stress and anxiety in mother. Music therapy is known to improve the milk secretion in mother, feeding, weight gain and outcome in babies. Many mothers are unable to provide sufficient amount of milk due to various reasons such as stress, anxiety, hormonal imbalance. Music improves endothelial function, as evaluated by flow-mediated vasodilation, according to a study by Michael Miller. The mechanism underlying the effect of positive emotions on endothelial Vaso-reactivity remains to be identified; one possible link is endorphin-mediated activation of endothelium- derived nitric oxide, an effect opposite to that observed when the potent vasoconstrictor endothelin- 1 is released in response to mental stress. Music therapy is a stress buster and has a positive effect on milk secretion. Music’s therapeutic value has been demonstrated in a few research based on physiological reactions to it in diverse situations. Music’s anxiolytic effects on patients prior to, during, and after surgery have long been known. This therapy helps in early recovery of babies from illness in NICU, increase weight gain and decrease hospital stay. It increases milk secretion in mother and increases bonding. We hypothesize that the postpartum stress in mothers can affect milk secretion and the same can be reduced with the use of music. Music therapy will enhance milk secretion in mothers causing better growth in baby and if music is there, it further enhances weight gain in baby.
Keywords
NICU, Stress, Anxiety, Music therapy, Feeding, Weight gain
Introduction
When babies are born preterm or suffer from some illness, they need to get admitted in NICU which can lead to stress and anxiety in mother. Maternal stress and anxiety is a known cause of inadequate milk secretion in mother which affect the growth and weight gain of baby [1]. Music therapy is known to improve the milk secretion in mother, feeding, weight gain and outcome in babies. Breast feeding is one of the best interventions needed for weight gain and proper growth in babies. Timely early breast feeding can decrease the mortality and morbidity in newly born babies. Breast feeding is directly linked with outcome of sick child. It not only affects growth, cognitive behaviour and brain development of child [2].
When baby is admitted in NICU then mother’s anxiety is tremendously increased and it hamper the secretion of milk in mother leading to poor feeding and inadequate weight gain in babies. Post-natal period is full of maternal stress. The stress, anxiety, poor diet and psychological factors of mother affect the milk secretion leading to lactational failure [1,3]. Music is the art of arranging sounds in time to produce a composition through the elements of melody, harmony, rhythm, and timbre. Music is performed with a vast range of instruments and vocal techniques. Music therapy has been found to be multimodal stimulation in term and pre term babies in NICUs. It has got a positive impact on brain development and auditory system of neonates. It gives stimulus for social and emotional development. Music therapy in babies improves feeding, reinforcement and can be a good multimodal approach to improve neonatal outcome [4,5]. Music has a physiological effect on health, development and mental status of individual leading to secretion of endorphins [6]. Music therapy is a stress buster and has a positive effect on milk secretion [7,8]. Maternal voice has got a positive role in bonding with the neonates. It decreases the stay in NICU and helps developing a good environment in NICU between babies and mother [9].
Music therapy is a stress buster and increases the weight gain, calorie intake in babies resulting in early discharge from hospital. It affects the better sucking leading to better feeding and early weight gain [10,11]. Different music modalities has different impact on health, feeding and weight gain of child with good outcome in NICUs. Instrumental music and mother’s voice both have been shown to improve the weight gain, sucking and feeding and early discharge of neonates from hospital [12].
Maternal voice is found to be a good stimulation for neonates. It can be recorded or can be directly sung during KMC or while caring and feeding of babies. Maternal voice has got behavioural, physiological and developmental effect on neonates which acts as a stimulus for the baby having a effect on heart rate, weight gain in NICU without having any adverse effect. It can proved to be a good bed side strategy in PNC ward for weight gain and neurodevelopment of baby [13].
The Music therapy lead to decrease in secretion of salivary cortisol level and makes the mood more joyful and decrease stress level which is directly linked to weight gain [14]. In very low birth weight babies live music have shown to improve weight gain [15] mostly by reducing stress level.
A woman's body is amazing. It has the power to not only create another human life, but also to provide all of the sustenance necessary for the child's growth and development. Breast milk production preparation starts before a woman is born and continues during her adolescence and pregnancy. Following the birth of a child, full production might last for months or even years. Breast milk is without a doubt the best diet for a human baby. Since scientists cannot make it in a laboratory. It can only be produced by a mother for her child.
Breast-feeding is the process by which the new born baby sucks the milk from the mother's brest. Whether the mother wants to breastfeed or not, the body of a woman produces breast milk involuntarily at first. After the first week, however, supply and demand determine the continued production of breast milk and the release of milk-forming hormones. A mother must either breastfeed or pump regularly if she wants to produce and retain a sufficient supply of milk for her baby. The pituitary gland secretes hormones such as prolactin and oxytocin. Prolactin is a hormone that tells your breast milk-producing glands to make milk. The let-down reflex is triggered by the hormone oxytocin, which causes milk to flow out. It constricts the alveoli and force the breast milk into the mammary ducts. After then, the infant consumes the milk. If the mother breastfeeds every one to three hours, she will empty her breasts and maintain her prolactin levels, as well as sustain the milk-stimulating stimulus. This time of maximum production of milk begins at the ninth day after delivery and it continues until nursing is completed. Sucking reflex of the new born baby plays important role in this process. It is one of the most important thing in the post natal period and the development of the new born babies. After the birth of the baby, the baby is kept near mother. That is called as the Rooming in. This gives psychological satisfaction to the mother that her baby is near to her that she kept 9 months in her womb. This procedure builds the special bonding between the mother and the new born baby. At this point the process of breastfeeding starts. The first milk of mother is called as colostrum which is very nutritious to the new born. The finest source of nourishment for babies is breast milk. It has a near-ideal ratio of vitamins, protein, and fat, which is just what a newborn need to survive — yet it's packaged It's more digestible than newborn formula. Antibodies in breast milk help the newborn's immune system fight infections and bacteria. Breastfeeding minimizes a newborn's risk of asthma and allergies. Furthermore, Ear infections, respiratory illnesses, and diarrhea are less common in newborns who are nursed solely during the first six months of their lives, without the use of any formula. They also reduce the likelihood of hospitalization and doctor visits. It contains immunoglobulin Ig A. This Ig A gives protection to the baby from the many infections in the neonatal age. Thus, development of the baby is very much important to the health of the baby. Normal development of the baby implies to the good nutrition, milestone achievement till the age and immunology. The impaired development of the baby may affect the further processes and immunology. Thus, breastfeeding is important and it should be started as soon as possible after the delivery. Breastfeeding has been related to higher IQ scores later in life in a number of studies. Physical proximity, skin-to-skin touch, and eye contact all help your infant feel secure and bond with you. Breastfed babies are more likely to gain the appropriate amount of weight as they grow up, rather than becoming overweight youngsters. Breastfeeding has also been linked to the prevention of SIDS, according to numerous research (sudden infant death syndrome). Diabetes, obesity, and some malignancies are all supposed to be reduced by it. Breastfeeding benefits both the mother and the baby. Breastfeeding burns additional calories, which can aid in the mother's weight loss after pregnancy. It secretes the hormone oxytocin, which aids in the return of the uterus to its pre-pregnancy size and may help to reduce post-partum uterine haemorrhage. Some studies have found that breastfeeding reduces the incidence of breast and ovarian cancer. It may also aid in osteoporosis prevention.
Because she doesn't have to buy and measure formula, sanitize nipples, or reheat bottles, the mother saves time and money. It also enables the mother to bond with her baby while spending quality time with her. Breast milk contributes to the baby's healthy weight gain. Breastfeeding also encourages a healthy weight increase in the baby and helps to prevent childhood obesity. Breastfeeding for more than 4 months was also linked to a lower risk of an infant being overweight or obese, according to certain research sources. This could be linked to the emergence of new gut bacteria. Breastfed newborns have higher levels of gut bacteria that are helpful. It's possible that these bacteria have an effect on fat storage. Newborns who are breastfed have higher levels of leptin in their bodies than babies who are fed formula. Leptin is a hormone that has a role in appetite regulation and fat storage. Breastfed newborns also control how much milk they consume. They are more adept at only eating till they are satisfied, which aids in the development of healthy eating habits. There are many parameters in the baby's normal growth and development i.e., milestone, weight, height, mental status, anthropology etc. among all these Weight is one of the most important measurable parameter of baby's growth. The pattern of weight gain in baby shows the nourishment what he has been getting from the mother's breastfeeding. Extra-uterine growth retardation is very common in low-birth-weight babies and is linked to poor Neuro-developmental outcome in later life [1]. Low birth weight babies may be preterm or as a result of IUGR (intrauterine growth retardation). Many maternal factors like nutritional status, antenatal checkup, maternal weight gain during pregnancy, complications in pregnancy and mother's systemic illnesses affect the weight of the baby [2,3]. In spite of state of art interventions and good neonatal care, low birth weight babies are at higher risk of getting infections, malnutrition with increase in mortality and morbidity [4].
Maternal stress or anxiety in postpartum period due to baby’s admission in NICU may decrease milk secretion depriving the baby from nutrition. The stress, anxiety, poor diet and psychological factors of mother are known to affect the milk secretion through oxytocin reflex leading to lactational failure which affects the growth, development and cognitive function of baby [5,6].
Many authors have noted music is a stress buster leading to relaxation and increases the weight gain, calorie intake in babies resulting in early discharge from hospital. It affects the quality of sucking leading to better feeding and early weight gain [7,8]. Mother’s voice is known to decrease pain perception in neonates while sampling or doing some procedures. It decreases total episodes of crying and bradycardia [9].
Some studies have shown that the baby's weight increase is aided by the mother's voice, which has physiological, behavioural, and emotional effects. According to several studies, maternal voice improved autonomic stability, resulting in improved heart rate and respiration, as well as weight gain in the baby [10].
Baby recognizes the voice of mother even as early as 4th day of life, may be because of prenatal effect, sensory and auditory response. The acoustic emission in womb can stimulate the child which helps in early recognition of voice [11]. Mother’s voice may be one of the factors affecting cognitive development, growth and weight gain of the baby. Mother’s singing for the babies has shown to increase bonding between mother and the child leading to increase in mood relaxation improving sensory skills, cognition, growth, development and health in premature babies [12]. Live and recorded maternal voice is found helpful in physiological and behavioural development with decreasing episodes of cardio-respiratory derangements which could play an important role in the weight gain of the baby [13]. Various studies recommend use of recorded mother’s voice in NICUs. There are definitely future needs of good studies using mother’s voice in the form of sound or music near the therapeutic level which will show statistical benefits in the baby [14]. We hypothesize that if music therapy is offered to babies during feeding by different means vocal or instrumental, it can definitely improve the weight gain pattern and more so if it is in mother’s live voice like lullaby by the mothers. Present study is to assess this hypothesis.
So we hypothesize that if music therapy is offered by different means and especially vocal, then it can definitely improve the weight gain pattern and outcome in neonatal life which has a positive outcome on mortality and morbidity in neonates. This study is to evaluate this hypothesis.
Aim and objectives
To assess the effect of music (vocal and instrumental) on preterm baby's weight gain. To assess the influence of music therapy in weight gain of the pre-term babies as compared to production without music. To assess the influence of vocal and instrumental music on pattern of weight gain of pre-term babies as compared to with no music and any music.
Type of study
Prospective, cross sectional, intervention study.
Place of study
Postnatal ward in AVBR hospital Sawangi Meghe, wardha.
Subjects
Preterm babies more than 30 weeks in NICU after acute phase is over and waiting for weight gain.
Inclusion criteria
Stable preterm new born more than15 days of life.
Baby must be on oral feeds.
Mother willing to participate in studies.
Exclusion criteria
Baby with major or multiple anomalies, ear anomalies, syndromic baby.
Baby on sedatives.
Mother not ready to participate.
Method-Once ethical committee approval is obtained, babies fulfilling selection criteria will be recruited from NICU after taking informed consent from parents.
Babies will be randomized into three groups using computer randomization.
In the first group the amount of weight gain of baby will be studied without music.
In second group the amount of weight gain of baby will be studied with any selected instrumental music.
In third group the amount of weight gain of baby will be studied with song inform of vocal music by mother
Each recruited baby will be studied for 7 days. Each mother and baby will be provided with ear phones and selected music will be played from mobile. Music will be played every time when baby is fed. The baby will be weight before starting the study and then every day at the same time. The weight will be recorded. Details (demographic and clinical) will be entered in a prevalidated proforma.
Statistical methods
Calculation of mean weight gain daily and cumulative will be calculated. Means in 3 groups will be compared using chi square test and p value of < 0.5 will be considered significant. Statistical software SPSS 21 will be used.
Implication
It is a cost effective and simple way to improve weight gain in baby. It can be easily followed by all the mothers. It will help.
Sample size
Title: Effect of music vocal and instrumental on weight gain in preterm baby.
Formula: Superiority study
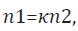
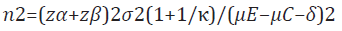
Fixed Scenario Elements
Distribution: Normal
Method: Exact
Number of sides: U
Null Difference: 0.2
Alpha: 0.05
Mean difference: 120
Standard deviation: 279
Group 1 weight: 1
Group 2 weight: 1
Nominal power: 0.8
Computed N total
Actual power: N total 0.801, 136
Considering 10% dropout rate, hence for one-sided hypothesis testing with the type I error level set to 5%, a total of 150 patients – 75 patients in each group – would be required in order to detect a clinically meaningful difference of 20% with 80% power and the standard deviation σ2=279
Reference: The effect of music on weight gain of preterm infants older than 32 weeks: a randomized clinical trial.
Discussion
Music’s advantages as an aural stimulant only just recently identified and scientifically verified. Lullaby in mother's voice has the potential in order to boost the benefits of multimodal stimulation, with one of its benefits being the promotion of homeostasis, which helps children tolerate stimuli.
The results for body weight gain in this study revealed that The Experimental Group's premature infants had a much higher mean than the Control Group's premature infants, which is critical for premature newborns because weight increase is linked to clinical stability and a shorter hospital stay. It is important to note that there were no significant differences in feeding methods or mean energy consumption across the groups studied. As a result, one of the hypotheses proposed in the Experimental Group for weight gain is that music can improve hunger and the sucking/swallowing process in children who are fed orally. Some research has looked into the relationship between music and Non-nutritive sucking was studied, and it was discovered that when music is playing, feeding rates increase. However, the authors do not specify whether the children had previously received oral nutrition, which could affect the pace of feeding.
Expected outcome
Comparison of the amount of baby's daily and cumulative weight gain with no music, vocal music and weight gain with any instrumental music.
Implication of the study – Music therapy if found to be effective will be a cost-effective method to improve milk secretion in mothers and weight gain in babies. It will help in better growth, to achieve full feeds early and good weight gain. It will also help mothers who stop breast feeding for lactational failure. It will improve breast feeding rates in India reducing infant mortality and morbidity and prevalence of malnutrition.
Mean and range of weight gain in babies without music.
Mean and range of weight gain with selected music.
Mean and range of weight gain with music in mothers’ voice.
Statistical difference in above 3 parameters.
Implications of the study
In the NICU music therapy can be a part of multimodal
approach to improve weight gain and development in preterm babies improving outcome.
It will help to achieve full feeds early with good weight gain so reduce the duration of stay in NICU and cost of management.
It will improve breast feeding practice in India reducing infant mortality and morbidity and also reduce prevalence of malnutrition in developing countries.
It is a cost effective and simple way to improve weight gain in baby. It can be easily followed by all the mothers. This study will further improve the normal growth and development the new born babies. This will also promote the breastfeeding.
Limitations of the study
The study has certain limitation such that it will not be able to cover mothers having psychological illness and or hearing problems or those who are not ready to participate in study.
Expected result
Music therapy will be said to be effective if subjects who will receive music therapy show significant increase (. p value of< 0.5will be taken as significant) in weight gain in baby. It is also expected that if mother listens to music of her own choice stress relief will be better and milk production will increase.
Generalizability
If this study is found to be effective it can be used easily anywhere like at home, in the hospital or in peripheral clinics also .The mobile is now a very handy tool available with all the mothers. They can make use of it easily to improve weight gain and which in turn will improve baby’s health. It will be an easy and cost effective method to improve child nutrition in India. If found effective music can turn out to be beneficial for baby also. Same music can help baby and mother both [15-19].
References
- Hopkinson JM, Schanler RJ, Garza C. Milk production by mothers of premature infants. Pediatrics 1988; 81:815-820.
- Vohr BR, Poindexter BB, Dusick AM, et al. Persistent beneficial effects of breast milk ingested in the neonatal intensive care unit on outcomes of extremely low birth weight infants at 30 months of age. Pediatrics 2007; 120:953.
- Hill PD, Ledbetter RJ, Kavanaugh KL. Breastfeeding patterns of low‐birth‐weight infants after hospital discharge. J Obstet Gynecol Neonatal Nurs 1997; 26:189-197.
- Fifer WP, Moon CM. The role of mother's voice in the organization of brain function in the newborn. Acta Paediatr Suppl 1994; 397:86-93.
- Standley J. Music therapy research in the NICU: An updated meta-analysis. Neonatal Netw 2012; 31:311-316.
- Miller M, Mangano CC, Beach V, et al. Divergent effects of joyful and anxiety-provoking music on endothelial vasoreactivity. Psychosom Med 2010; 72:354-356.
- JF Landreth, HF Landreth. Effects of music on physiological response. J Res Music Educ 1974; 22:4–12.
- Vianna MN, Barbosa AP, Carvalhaes AS, et al. Music therapy may increase breastfeeding rates among mothers of premature newborns: A randomized controlled trial. J Pediatr 2011; 87:206-212.
- Cevasco AM. The effects of mother’s singing on full-term and preterm infants and maternal emotional responses. J Music Ther 2008; 45:273-306.
- Caine J. The effects of music on the selected stress behaviors, weight, caloric and formula intake, and length of hospital stay of premature and low birth weight neonates in a newborn intensive care unit. J Music Ther 1991; 28:180-192.
- Van der Heijden MJ, Oliai Araghi S, Jeekel J, et al. Do hospitalized premature infants benefit from music interventions? A systematic review of randomized controlled trials. PloS One 2016; 11:e0161848.
- Alay B, Esenay FI. The clinical effect of classical music and lullaby on term babies in neonatal intensive care unit: A randomised controlled trial. J Pak Med Assoc 2019; 69:459-463.
- Williamson S, McGrath JM. What are the effects of the maternal voice on preterm infants in the NICU? Adv Neonatal Care 2019; 19:294-310.
- Hasanah I, Mulatsih S, Haryanti F, et al. Effect of music therapy on cortisol as a stress biomarker in children undergoing IV-line insertion. J Taibah Univ Med Sci 2020; 15:238-243.
- Schwilling D, Vogeser M, Kirchhoff F, et al. Live music reduces stress levels in very low‐birthweight infants. Acta Paediatr 2015; 104:360-367.
- Gadegone A, Daigavane S, Walavalkar R. Effect of music on blood pressure and heart rate in patients undergoing cataract extraction surgery. J Evol Med Dent Sci 2021; 10:1474–1478.
- Garg M, Mohale S. Prevalence of Metabolic Obesity Normal Weight (MONW) in cardiovascular disease patients--A hospital-based case control study. J Evol Med Dent Sci 2020; 9:2427-2432.
- Collaborators LB, Pepito VC. Mapping local patterns of childhood overweight and wasting in low-and middle-income countries between 2000 and 2017. Nature Med 2020; 26:750–759.
- Pusdekar YV, Patel AB, Kurhe KG, et al. Rates and risk factors for preterm birth and low birthweight in the global network sites in six low-and low middle-income countries. Reproductive Health 2020; 17:1-6.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Indexed at, Google ScholarCross Ref
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Indexed atGoogle Scholar, Cross Ref
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Author Info
Mitali Agrawal1*, Bhavana Lakhkar1 and Mahaveer Lakhra2
1Department of Pediatrics, Jawaharlal Nehru Medical College, Datta Meghe Institute of Medical Sciences, Wardha, India2Department of Neonatology, Jawaharlal Nehru Medical College, Datta Meghe Institute of Medical Sciences, Sawangi (M), Wardha, Maharashtra, India
Received: 28-Nov-2022, Manuscript No. jrmds-22-77130; , Pre QC No. jrmds-22-77130(PQ); Editor assigned: 30-Nov-2022, Pre QC No. jrmds-22-77130(PQ); Reviewed: 15-Dec-2022, QC No. jrmds-22-77130(Q); Revised: 19-Dec-2022, Manuscript No. jrmds-22-77130(R); Published: 26-Dec-2022
