Research - (2021) Volume 9, Issue 7
Intranasal Dexmedetomidine Versus Oral Midazolam as Premedication in Anaesthesia in Children
*Correspondence: R Purushotham, Department of Anaesthesiology, Pain Medicine and Critical Care, Sree Balaji Medical College & Hospital Affiliated to Bharath Institute of Higher Education and Research, India, Email:
Abstract
Only patients belonging to ASA I & II were chosen for the study. There was mild reduction m heart rate after administration of intranasal dexmedetomidine compared to oral midazolam. Sedation score of 3 and 4 were 73 % in Group A whereas 30 % in Group B (Oral Midazolam). At 20 mins, 60% were achieving score of 1 & 2 in Group A whereas 16% in Group B. at 30 mins, score 1 and 2 was about 80% in Group A and 43 % in Group B. Behaviour Scores of 1 and 2 at 10, 20 30 mins in Group A were 37%, 74%, 83% and 17%, 43%, 57% for Group B.
Keywords
Dexmedetomidine, Midazolam, PremedicationIntroduction
Midazolam is a very common preanesthetic medication which is replaced by Dexmedetomidine an alpha-2 agonists in recent years. Many clinical trials have been performed to determine the efficacy of dexmedetomidine versus midazolam. But still no promising evidence are achieved to prove which agent is superior over other. Therefore, this study was conducted to compare efficacy & clinical effects of intranasal dexmedetomidine and oral midazolam as a preanaesthetic medication in children undergoing minor elective surgery [1-3].Methodology
Children of age group of 2- to 12-year-old was taken for the study and categorized in to two groups Group A were administered with intranasal dexmedetomidine with a dosage of1 μg/kg body weight, 45 minutes prior to surgery and Group B with Oral Midazol of 0.5mg /kg body weight in 10 ml apple juice 30 minutes before surgery. After which the patient's blood pressure, heart rate, oxygen saturation was recorded at induction of anaesthesia. Sedation was assessed every 10 minutes with 6 point Modified observer's assessment of alertness / sedation scale. Behavioral changes and hemodynamic changes were also assessed.Results
resizable=yes,width=500,height=330')" class="thumbnail">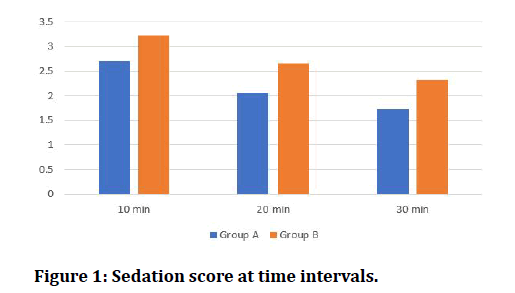
Figure 1: Sedation score at time intervals.
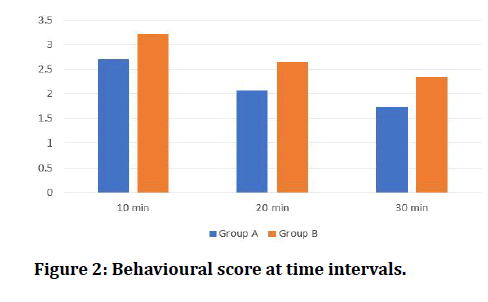
Figure 2: Behavioural score at time intervals.
Discussion and Conclusion
Midazolam is a versatile drug in general anaesthesia, but it is not ideal drug for premedication because of its adverse effects of restlessness, paradoxical reaction, negative postoperative behavioural changes. When comparing the effect of this drug with another similar agent like dexmedetomidine, the sedation scores at 10, 20 and 30 minutes are better with intranasal dexmedetomidine, which are statistically significant (p value is 0.0082, 0.0487 and 0.0351 respectively). statistically significant. The post-operative agitation was less with intranasal dexmedetomidine than with oral midazolam like study done by Schmidt et al. [4-9].
References
- Ball C, Westhorpe RN. The history of premedication. Anaesth Intensive Care 2011; 39:991.
- Bacon DR, Francis Hoeffer McMechan. Creater of modern anaesthesiology. Anesth Analg 2012; 115:1393-400.
- Mostafa GM, Khaled MM. Premedication with intranasal dexmedetomidine, midazolam and ketamine for children undergoing bone marrow biopsy and aspirate. Egyptian J Anaesthesia 2013; 29:131-135.
- Schmidt AP, Valinetti EA, Bandeira D, et al. Effects of preanesthetic administration of midazolam, clonidine, or dexmedetomidine on postoperative pain and anxiety in children. Paediatr Anaesth 2007; 17:667-74.
- Madej TH, Paasuke RT. Anaesthetic premedication: aims, assessment and methods. Can J Anaesth 1987; 34:259.
- White PF. Pharmacologic and clinical aspects of preoperative medication. Anesth Analg 1986; 65:963e74.
- Kamibayashi T, Maze M. Clinical uses of a2-adrenergic agonists. Anesthesiol 2000; 93:1345-1349.
- Wagner DS, Brummett CM. Dexmedetomidine: As safe as safe can be. Semin Anesth Perioper Med Pain 2006; 25:77-83.
- Shagufta Naaz, Erum Ozair. Dexmedetomidine in current anaesthesia practice- A review. J Clin Diagnost Res 2014; 8:GE0l- GE04.
Author Info
Department of Anaesthesiology, Pain Medicine and Critical Care, Sree Balaji Medical College & Hospital Affiliated to Bharath Institute of Higher Education and Research, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, IndiaCitation: R Purushotham,Intranasal Dexmedetomidine Versus Oral Midazolam as Premedication in Anaesthesia in Children, J Res Med Dent Sci, 2021, 9(7): 457-459
Received: 12-Jul-2021 Accepted: 28-Jul-2021
