Case Report - (2022) Volume 10, Issue 9
Skin Flickering Sign: A New Clinical Sign for Differentiating Pre-Eruptive Herpes Zoster from Other Causes of Unilateral Pain
Haidar Hassan Al-Ameri1* and Hieder Al-Shami2
*Correspondence: Dr. Haidar Hassan Al-Ameri, Department of Neurosurgery, Kut University College, Kut, Wasit, Iraq, Email:
Abstract
Diagnosing herpes zoster before the appearance of eruption is very challenging. We report a new clinical sign that can aid in the diagnosis of herpes zoster in the pre eruptive phase and in exclusion of other types of pain. The skin flickering sign (or Haidar sign) is regarded positive when patient feels an increase in the intensity of pain or paresthesia during flickering of skin. Skin flickering sign is a simple, reproducible and diagnostic sign for differentiating between herpes zoster pain or allodynia and any other cause of unilateral pain including pain of visceral origin. This sign will aid physicians in the diagnosis of pre-eruptive herpes zoster or at least in raising the suspicion of its presence thus proceeding to the expensive not widely available laboratory tests
Keywords
Paresthesia, Allodynia, Herpes zoster, Laboratory tests, SuspicionIntroduction
Herpes zoster is usually manifested as a unilateral vesicular eruption, onset of disease is heralded by a pain within the dermatome which may proceed the lesion by 48-72 hours [1-4] within the first days when there is no skin eruption, there is a few physical signs, this makes diagnosing herpes zoster very difficult [5,6], actually it is the cutaneous eruption what makes herpes zoster diagnosis obvious [7,8]. The most commonly affected dermatomes are T3-L3 dermatomes so pain of herpes zoster can mimic even acute abdomen and may leads even to unnecessary surgical exploration. This was illustrated in a study of 121 negative emergency laparotomies, in which three patients had a diagnosis of herpes zoster [9].
Our case report recorded a new clinical sign to differentiate pre-eruptive herpes zoster pain from other types of pain including pain of visceral origin.
Description of maneuver
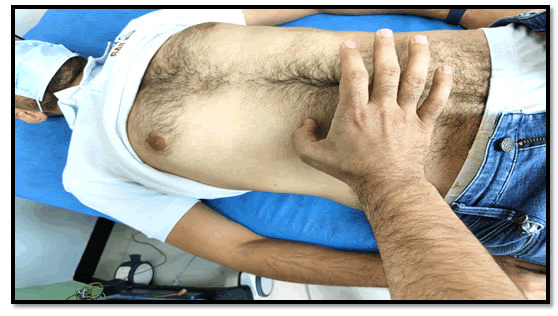
The steps for applying skin flickering sign (haidar sign) are simple and require no instruments. First, in patients presented with unilateral pain specially elderlies or immunosuppressed patients in which we had to exclude herpes zoster, we can apply a flickering movement to the affected area with the tip or side of our right thumb if pain or parasethesia increase in intensity, this donate a positive sign (Figure 1), to further more ensure positivity we can gently take a skin fold from the affected area with thumb and forefingers of our left hand ensuring that it involves more than single dermatome. If the cause of the pain is pre eruptive herpes zoster, this flickering movement will increase the intensity of pain or paresthesia in the stimulated area (with or without facial grimace or withdrawal reflex) and the signs is regarded as a positive, while in visceral pain or other causes of unilateral pain the flickering movement will not change the intensity of pain. The explanation is simple; this pain is of cutaneous origin in herpes zoster due to hyperalgesia effect of the affected dermatome while it is not in cases of visceral or peritoneal origin of the pain.
Figure 1: Apply a flickering movement to the affected area with the tip or side of our right thumb.
Case Presentation
We collected five cases in which this sign was a clear cut to differentiate between visceral and pre eruptive HZ pain. All cases were consulted for diagnosis mismatch between complain and sonographic findings of either clear healthy gallbladder or surgically removed gallbladder. All cases pose a risk factor for either cholecystitis or herpes zoster infection. However, the dermatomal representation of pain is the primary factor confounding the diagnoses. All these cases underwent a skin flickering method and found to be positive. A diagnosis of neuralgia was aided by this method. Therapeutic trial thereafter revealed an improvement of pain over 3 months with subsequent need for interventional pain management for the 4th and 5th cases [Table 1].
| No | gender | Age | PMH | D.D | Affected dermatome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | F | 59 | MD, HTN, GERD, chronic cholecystitis | Bilary colic, IBD (RHC) | Right T7 |
| 2 | F | 72 | HTN, DM, CVA | Abdominal pain (RHC) | Right T6 |
| 3 | M | 55 | Obesity, hypercholesterolemia | RHC | Right T7-8 |
| 4 | F | 45 | Obesity | RHC | Right T8 |
| 5 | M | 66 | DM, HTN, Previous cholecystectomy | RHC | Right T7 |
Table 1: Criteria of cases reported.
Discussion
In our case report, we confirmed a diagnosis of a pre-eruptive herpes zoster misdiagnosed as a visceral pain focusing by a new method of examination. We focused on differentiating herpes zoster from other causes of right hypochondrial pain because of the high frequency of these dermatomes involvement in herpes zoster and high frequency of other causes of right hypochondrial pain. This method is quietly simple, reproducible and diagnostic.
Our method is completely based on the pathophysiology of herpes zoster; it emerges in the peripheral and central neurons [10]. Damage of these neurons by inflammatory by product resulting in a lower threshold of pain action potential, spontaneous discharge, and disproportionate responses to stimuli [11]. All of these previously mentioned are described as allodynia [12,13]. Patient with HZ has five types of sensations:
- Constant pain without a stimulus
- Intermittent pain
- Pain brought on by a stimulus (hyperalgesia)
- Paresthesia
Misdiagnosis of neurological diseases is an everyday story in clinical practice it has many ethical, clinical and economic drawbacks [14,15]. Fan and colleagues reported a case with herpes zoster misdiagnosed as acute appendicitis [16]. Monib and Emre reported a case with acute abdomen which lately diagnosed with herpes zoster presented with acute left upper abdominal quadrant pain [17].
This is due to variety of causes. First, lower attention of clinical knowledge in the era of now technology in diagnostic imaging [18]. Second, over crowdedness of outpatient clinics shortened time of consultation. Third, insidiousnature of disease with and its ability to overlap with other diseases [16,19,20]. Physicians should be aware of his/her patient's complain. Trying to update his/her knowledge to provide the best service ever.
Our clinical sign offers the opportunity to physicians, neurologists, dermatologists, neurosurgeons and pain management clinicians to differentiate between visceral pain and dermatomal pain due to post herpetic neuralgia. This will be of great value in decreasing frequency of misdiagnosis of HZ. The authors are planning to conduct a wide sample randomized study in the future.
Conclusion
Skin flickering sign (or Haidar Sign) is a simple, reproducible and diagnostic sign for differentiating between visceral pain and postherpetic pain. This sign will aid physicians in the diagnosis of pre-eruptive herpes zoster or at least in raising the suspicion of its presence and thus choosing patients eligible for confirmatory immunological tests for herpes zoster in pre eruptive phase.
Acknowledgment
The authors decided to name the skin flickering sign as (Hayder Sign) as another name for it.
References
- Kasper, Dennis L, Harrison TR, et al. Principles of Internal Medicine.McGraw-Hill Medical Publishing, 16th Edition,New York, 2607.
- Rimland D, Moanna A. Increasing incidence of herpes zoster among veterans. Clin Infect Dis 2010; 50:1000-1005.
- Insinga RP, Itzler RF, Pellissier JM, et al. The incidence of herpes zoster in a United States administrative database. J Gen Intern Med 2005; 20:748-753.
- Gupta G, Lautenbach E, Lewis JD. Incidence and risk factors for herpes zoster among patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2006; 4:1483-1490.
- Munoz L, Balmana J, Martino R, et al. Abdominal pain as the initial symptom of visceral varicella zoster infection in hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients. Med Clin (Barc) 1998; 111:19–22.
- Oxman MN, Levin MJ, Johnson GR, et al. A vaccine to prevent herpes zoster and postherpetic neuralgia in older adults. N Engl Med 2005; 352:2271–2284.
- Rubben A, Baron JM, Grussendorf-Conen EI. Routine detection of herpes simplex virus and varicella zoster virus by polymerase chain reaction reveals that initial herpes zoster is frequently misdiagnosed as herpes simplex. Br J Dermatol 1997; 137:259–261.
- Kalman CM, Laskin OL. Herpes zoster and zosteriform herpes simplex virus infections in immunocompetent adults. Am J Med 1986; 81:775–778.
- Magdiev T, Kuznetsov VD, Shipilov VA, et al. Erroneous laparotomy in emergency surgery. Khirurgiia (Mosk) 1991; 11:118–122.
- Backonja MM. Postherpetic neuralgia. In: Neurobiology of Disease. Elsevier, 3rd ed, 2007: 1031-1037.
- Baron R, Wasner G. Prevention and treatment of postherpetic neuralgia. The Lancet 2006; 367:186-188.
- Sandkühler J. Models and mechanisms of hyperalgesia and allodynia. Physiol Rev 2009; 89:707-758.
- Jensen TS, Finnerup NB. Allodynia and hyperalgesia in neuropathic pain: clinical manifestations and mechanisms. Lancet Neurol 2014; 13:924-935.
- Cooper A, Carson-Stevens A, Cooke M, et al. Learning from diagnostic errors to improve patient safety when GPs work in or alongside emergency departments: incorporating realist methodology into patient safety incident report analysis. BMC emerg med 2021; 21:139.
- Fan Z, Pan J, Zhang Y, et al. Herpes zoster mimicking as acute appendicitis: A case report. Int J Clin Exp Med 2016; 9:5064-5067.
- Monib S, Pakdemirli E. Shingles (Herpes Zoster) Mimicking Acute Abdomen. Cureus 2020; 12:10-12.
- Roelandt JRTC. The decline of our physical examination skills: Is echocardiography to blame? Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging 2014; 15:249-252.
- Babatabar-Darzi H, Jafari-Iraqi I, Mahmoudi H, et al. Overcrowding management and patient safety: An application of the stabilization model. Iran J Nurs Midwifery Res 2020; 25:382.
- Pope JV, Edlow JA. Avoiding Misdiagnosis in Patients with Neurological Emergencies. Emerg Med Int 2012; 1-10.
- Bekircan-Kurt CE, Inan B, Bulut O, et al. Neuropathic Pain Frequency in Neurology Outpatients: A Multicenter Study. Noro psikiyatri arsivi 2021; 58:257-260.
Author Info
Haidar Hassan Al-Ameri1* and Hieder Al-Shami2
1Department of Neurosurgery, Kut University College, Kut, Wasit, Iraq2Department of Neurosurgery, Al-Hussein University Hospital, Cairo, Egypt
Citation: Haidar Hassan Al-Ameri, Hieder Al-Shami, Skin Flickering Sign: A New Clinical Sign for Differentiating Pre- Eruptive Herpes Zoster from Other Causes of Unilateral Pain, J Res Med Dent Sci, 2022, 10 (9): 191-193.
Received: 04-Jul-2022, Manuscript No. JRMDS-22-62941; , Pre QC No. JRMDS-22-62941(PQ); Editor assigned: 07-Jul-2022, Pre QC No. JRMDS-22-62941(PQ); Reviewed: 21-Jul-2022, QC No. JRMDS-22-62941; Revised: 05-Sep-2022, Manuscript No. JRMDS-22-62941(R); Published: 12-Sep-2022