Research - (2020) Advances in Dental Surgery
Correlation of Protein Level with the Severity of Early Childhood Caries
Anitha Jayakumar, Deepa Gurunathan* and Mebin George Mathew
*Correspondence: Deepa Gurunathan, Department of Pediatric and Preventive Dentistry, Saveetha Dental College, Saveetha Institute of Medical and Technical Sciences, Saveetha University, Chennai, India, Email:
Abstract
The present study was undertaken to correlate the serum albumin level with severity of early childhood caries. 56 Children with early childhood caries were recruited from outpatient reporting to the Department of Pediatric and Preventive Dentistry. Oral examination was done. dmft index was scored and severity of ECC was recorded (Wyne’s classification). Blood samples were collected by venipuncture and the serum albumin level was estimated. Statistical analysis was done using SPSS vs. 23.0 Mean value of serum albumin level was found to be higher in the children with type 1 (mild to moderate) ECC and lower in type 3 (severe) ECC. Within the limits of our study we found that the relationship between the protein level and the early childhood caries was not statistically significant in this study. However lower serum albumin level was found in the children with type 3 (severe) ECC.
Keywords
Early childhood caries and albumin levels
Introduction
ECC is the most common chronic disease of childhood. Apart from the classic etiological triad for caries, it is a complex disease influenced by health determinants and environment. Our understanding of the systemic influence of ECC on overall health is limited. There are studies which support that those with ECC are also deficient in vitamins and nutrients [1]. The uptake of serum albumin by maturation stage rodent enamel results in albumin entering the enamel by extravasations in vivo produces incomplete tissue maturation, resulting in white opaque appearance on eruption [2]. Albumin is a serum protein that can be used as an additional indicator of overall nutritional status and malnutrition [3]. Our department is passionate about childcare; we have published numerous high quality articles in this domain over the past 3 years [4-17]. Hence this study was undertaken to determine the association between the albumin level and the severity of early childhood caries.
Materials and Methods
This observational study was carried out in the department of Pedodontic and Preventive Dentistry of Saveetha dental college, Chennai. Ethical clearance was obtained from the institutional scientific review board SRB/ STPG15/41. 56 Children with early childhood caries were recruited from outpatient reporting to the department. Children less than 72 months of age reporting to the department were included in the study. Children with any systemic conditions; usage of prolonged medications; usage of any multivitamin supplementation; medically compromised children are excluded from the study. The data related to the presence of decayed, missing and filled surface (dmfs); decayed, missing and filled teeth (dmft) were recorded and the severity of early childhood caries were assessed based on Wyne’s classification [18] (Table 1). After getting concern from the parents, 2ml of blood samples were collected from the participants by venipuncture. Blood samples were collected either from anticubital fossa or metacarpal veins in children by the experienced nurses or lab technicians. The collected samples were kept in the test tubes and were transported to the diagnostic centers on the same day. In the diagnostic center, the serum albumin levels were estimated. Statistical data analysis was performed using SPSS software version 23.0.
| Type I | Mild to Moderate ECC (Isolated carious lesion(s) involving molars and /or incisors) |
| Type II | Moderate to severe ECC (Labiolingual carious lesions affecting maxillary incisors with or without molar caries and unaffected mandibular incisors) |
| Type III | Severe ECC (Carious lesions affecting all teeth including lower incisors) |
Table 1: Wyne’s classification.
Results
The mean value of albumin level in mild to moderate ECC (Type-1) group is 4.57 where as the mean value of albumin level in severe ECC (Type-3) group is 4.39. The mean value of albumin level in moderate to severe ECC (Type- 2) group is 4.52 (Figure 1).
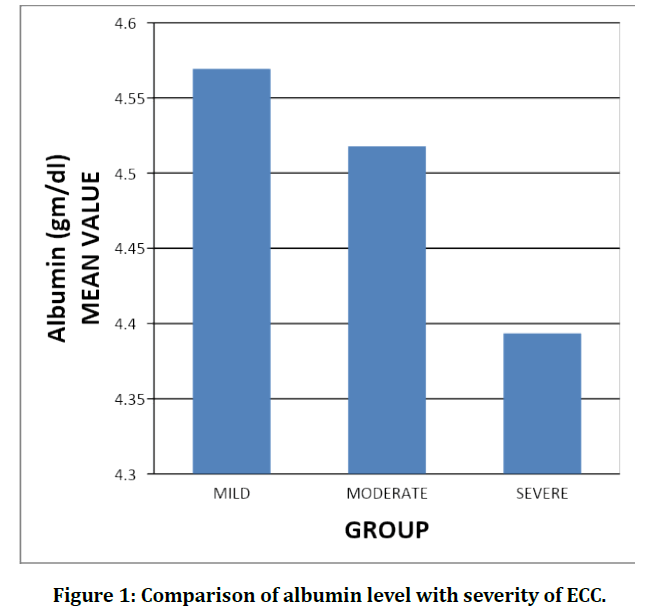
Figure 1: Comparison of albumin level with severity of ECC.
Discussion
The relationship between the protein level and the early childhood caries was not statistically significant in this study. Mean value of serum albumin level was found to be higher in the children with type 1 (mild to moderate) ECC. A study by Scroth et al. [1] concluded that children with S-ECC had significantly lower levels of serum albumin than the children without ECC which is similar to the findings of the present study.
S-ECC seems to be a significant risk factor for the malnutrition. A deficiency in the serum albumin protein levels in conjugation with undesirable vitamin D, PTH and calcium levels may suggest that the children with severe early childhood caries have nutritional deficiencies [1]. Hence the dentists should consider that children with early childhood caries are at risk for nutritional deficiencies which may affect long-term health and well-being [19].
Conclusion
The relationship between the protein level and the early childhood caries was not statistically significant in this study. In the present study the serum albumin level was found to be higher in the children with type 1 (mild to moderate) ECC and lower serum albumin level was found in the children with type 3 (severe) ECC.
References
- Schroth RJ, Levi JA, Sellers EA, et al. Vitamin D status of children with severe early childhood caries: A case–control study. BMC Pediatr 2013; 13:174.
- Robinson C, Kirkham J, Brookes SJ, et al. The role of albumin in developing rodent dental enamel: A possible explanation for white spot hypoplasia. J Dent Res 1992; 71: 1270–1274.
- https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/bf6c/9ce5a629046efd4f454f82f5a52797103e1c.pdf
- JeevananDan G. Kedo-S paediatric rotary files for root canal preparation in primary teeth-Case report. J Clin Diagn Res 2017; 11:ZR03.
- Govindaraju L, Jeevanandan G, Subramanian EMG, et al. Comparison of quality of obturation and instrumentation time using hand files and two rotary file systems in primary molars: A single-blinded randomized controlled trial. Eur J Dentistry 2017; 11:376–379.
- Govindaraju L, Jeevanandan G, Subramanian EMG, et al. Knowledge and practice of rotary instrumentation in primary teeth among indian dentists: A questionnaire survey. J Inter Oral Health 2017; 9:45.
- Somasundaram S, Ravi K, Rajapandian K, et al. Fluoride content of bottled drinking water in Chennai, Tamilnadu. J Clin Diagn Res 2015; 9: ZC32.
- Jeevanandan G, Govindaraju L. Clinical comparison of Kedo-S paediatric rotary files vs. manual instrumentation for root canal preparation in primary molars: A double blinded randomized clinical trial. Eur Arch Paediatr Dent 2018; 19:273–278.
- Govindaraju L, Jeevanandan G, Subramanian E, et al. Clinical evaluation of quality of obturation and instrumentation time using two modified rotary file systems with manual instrumentation in primary teeth. J Clin Diagn Res 2017; 11:ZC55–ZC58.
- Ravikumar D, Jeevanandan G, Subramanian EMG, et al. Evaluation of knowledge among general dentists in treatment of traumatic injuries in primary teeth: A cross-sectional questionnaire study. Eur J Dent 2017; 11:232–237.
- Panchal V, Jeevanandan G, Subramanian EMG, et al. Comparison of instrumentation time and obturation quality between hand K-file, H-files, and rotary Kedo-S in root canal treatment of primary teeth: A randomized controlled trial. J Indian Soc Pedod Prev Dent 2019; 37:75.
- Christabel SL, Gurunathan D. Prevalence of type of frenal attachment and morphology of frenum in children, Chennai, Tamil Nadu. World J Dent 2015; 6:203–207.
- Packiri S, Gurunathan D, Selvarasu K, et al. Management of paediatric oral ranula: A systematic review. J Clin Diagn Res 2017; 11:ZE06.
- Gurunathan D, Shanmugaavel AK. Dental neglect among children in Chennai. J Indian Soc Pedod Prev Dent 2016; 34:364.
- GovinDaraju L, Gurunathan D. Effectiveness of Chewable Toothbrush in children-A prospective clinical study. J Clin Diagn Res 2017; 11:ZC31.
- Subramanyam D, Gurunathan D, Gaayathri R, et al. Comparative evaluation of salivary malondialdehyde levels as a marker of lipid peroxidation in early childhood caries. Eur J Dentistry 2018; 12:67–70.
- Ramakrishnan M, Bhurki M. Fluoride, fluoridated toothpaste efficacy and its safety in children-Review. Int J Pharma Res 2018; 10:109-114.
- Wyne AH. Early childhood caries: Nomenclature and case definition. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol 1999; 27:313–315.
- Clarke M, Locker D, Berall G, et al. Malnourishment in a population of young children with severe early childhood caries. Pediatr Dent 2006; 28:254–259.
Author Info
Anitha Jayakumar, Deepa Gurunathan* and Mebin George Mathew
Department of Pediatric and Preventive Dentistry, Saveetha Dental College, Saveetha Institute of Medical and Technical Sciences, Saveetha University, Chennai, IndiaCitation: Anitha Jayakumar, Deepa Gurunathan, Mebin George Mathew, Correlation of Protein Level with the Severity of Early Childhood Caries – An Observational Study, J Res Med Dent Sci, 2020, 8 (7): 534-536.
Received: 02-Nov-2020 Accepted: 20-Nov-2020 Published: 27-Nov-2020
