Research - (2020) Advances in Dental Surgery
Determination of Sex by Occipital Condyle Intercondylar Distance and Foramen Magnum Among South Indian Population
Aksha Sharen A and Karthik Ganesh Mohanraj*
*Correspondence: Karthik Ganesh Mohanraj, Department of Anatomy, Saveetha Dental College, Saveetha Institute of Medical and Technical Sciences (SIMATS), Saveetha University, Chennai, India, Email:
Abstract
The morphometric evaluation of occipital condyle, intercondylar distance and foramen magnum is clinically interesting because of its relation with its contents. Occipital condyles are two bony elevations present on either side of foramen magnum in the base of the skull which articulates with the superior articular facet of the atlas vertebra, connecting the skull with the vertebral column. The diameters of the foramen magnum are very important because the vital structures passing through it and for sex determination of skulls. The aim of the present study is to determine the sex by occipital condyle, inter-condylar distance and foramen magnum among South Indian population. The study used dry skulls of south Indian populations and vernier calipers for measurement. Completely ossified 50 adult human dry skulls of unknown age and sex were taken from the Department of Anatomy of saveetha dental college, chennai were used for the study. The skull samples which were deformed were excluded from the study the length and breadth of occipital condyles, distance from each occipital condyle, dimension of foramen magnum were measured using a digital vernier caliper graded upto 0.01mm. Observations made were tabulated. According to the present study The average diameter of the occipital condyles of male was found to be 13.72 ± 0.42 mm. The average diameter of the occipital condyles of female was found to be 12.82 ± 0.54 mm. The average length of the intercondylar distance in male was found to be 30.41 ± 4.75 mm. The average length of the intercondylar distance in female was found to be 27.76 ± 3.88 mm. The average diameter of the foramen magnum in male was found to be 31.52 ± 5.14 mm. The average diameter of the foramen magnum in female was found to be 29.18 ± 4.32 mm respectively. Detailed morphometric analysis of occipital condyle, intercondylar distance foramen magnumwill help in the estimation of sex though all the parameters doesn’t proove to be effective but it can serve as an additional criteria in case of skull obtained with damages on the cranial bones. This study will be useful also for the anatomist, neurosurgeon, radiologist, and morphologists’ clinical anatomists to carry out further detailed morphometric analysis.
Keywords
Morphometry, Occipital condyle, Intercondylar distance, Foramen magnum, Sex determination
Introduction
Occipital condyles (OC) are present on either aspect of foramen magnum and are related to many important structures which emerge out from the surrounding foramen such as jugular foramen, hypoglossal foramen and posterior condylar foramen [1–3]. It articulates with superior articular facets of atlas to form atlantooccipital joint Occipital condyles are considered to be oval in shape. It is aligned obliquely in such a way that the anterior end of it is closer to each other when compared with the posterior end. On the medial aspect of each condyle a large foramen magnum is present which communicates above with the posterior cranial fossa. It contains the lower end of medulla oblongata, meninges, vertebral artery, spinal accessory nerve, apical ligament and tectorial membrane [4,5]. Knowledge of dimensions of occipital condyles and its relation with neighbouring foramen is important for the neurosurgeons operating in this region [6,7]. Knowledge of morphometry of the Occipital condyle may therefore be useful in decisions regarding extent and direction of condylar drilling to avoid occipito-cervical destabilization and inadvertent injury of the hypoglossal canal neurovascular structures [8–10]. The intercondylar distance however is a stable and a bony landmark that remains fairly static throughout life [11–13].
The foramen magnum is situated in an anteromedial position in the occipital bone and communicates into the posterior cranial fossa. It is oval in shape which is wider from behind. It is greatest in its dimensions anteroposteriorly. Posterior part of foramen magnum known as neurovascular compartment which contains the lower end of the medulla oblongata, meninges, cerebrospinal fluid, vertebral vessels and the accessory nerves; anterior part of it is known as osseo-ligamental compartment through which the cruciate ligament, apical ligament of the dens and the tectorial membrane pass and attach to the internal aspect of basi-occiput [14–16]. The knowledge of the dimensions and shape of the foramen Magnum has important clinical implications in the prognosis and treatment of various neurological pathologies like Arnold Chiari syndrome, and posterior cranial fossa lesions [17–19]. Evaluation of foramen magnum is important for neurosurgical approaches, forensic, radiological evaluations and for evolutionary studies [20–22].
We therefore sought to determine the dimensions of the occipital condyle, intercondylar distance, foramen magnum in the dry human skulls. The aim of the present study was to determine the sex by occipital condyle, inter-condylar distance and foramen magnum among South Indian population.
Materials and Methods
The present study was carried out on 100 occipital condyles, foramen magnum, intercondylar distance of 50 dry adult skulls. Damaged and broken skulls were not included. The following 7 parameters of the occipital condyles, intercondylar distance, foramen magnum were mea- sured and analysed on both the sides. The collected data were entered and analyzed using the Statistical Package of Social Science (SPSS) program for Windows SPSS for analysis. The mean and standard deviations were calculated. The comparison of various dimensions of the right and left sides was performed using Student’s t-test and p-value was calculated. Between the male and female skulls, statistical significance is determined with p<0.05 for the parameters like dimensions of occipital condyle, foramen magnum and for the intercondylar distance. Data were graphically represented by bar diagrams.
Inclusion criteria
Skulls without any fracture and gross abnormalities, absence of fractures in the foramen magnum, occipital condyle area were considered for evaluation.
Exclusion criteria
Fracture involving the base of the cranium. Congenital anomalies of the skull trauma, bone pathologies and extensive fractures.
Results
The morphometric analyses of occipital condyle, intercondylar distance and foramen magnum consisting a total of 7 parameters were analyzed. The average length and breadth of occipital condyle of the right side in male was found to be 18.77 ± 0.39 mm and 8.86± 0.76 mm respectively. The average length and breadth of occipital condyle of the left side in male was found to be 18.61 ± 0.52 mm and 8.62 ± 0.23 mm respectively. The average length and breadth of occipital condyle of the right side in females was found to be 17.03 ± 0.71 mm and 8.43 ± 0.42 mm respectively. The average length and breadth of occipital condyle of the left side in females was found to be 17.73 ± 0.34 mm and 12.93 ± 0.59 mm respectively. The comparison of average length and breadth of occipital condyle in male and female is shown in Figures 1-4. The average diameter of the occipital condyles of male was found to be 13.72 ± 0.42 mm. The average diameter of the occipital condyles of females was found to be 12.82 ± 0.54 mm.
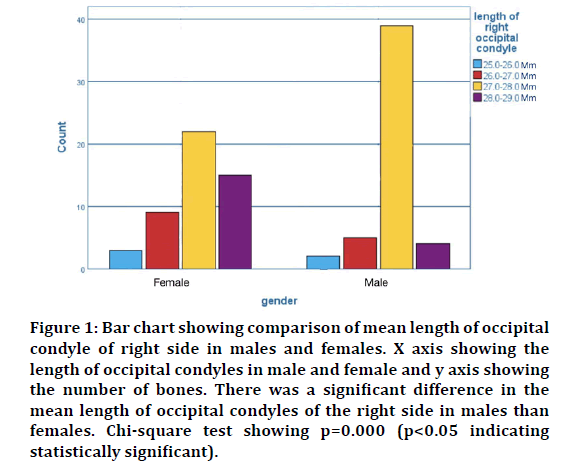
Figure 1: Bar chart showing comparison of mean length of occipital condyle of right side in males and females. X axis showing the length of occipital condyles in male and female and y axis showing the number of bones. There was a significant difference in the mean length of occipital condyles of the right side in males than females. Chi-square test showing p=0.000 (p<0.05 indicating statistically significant).
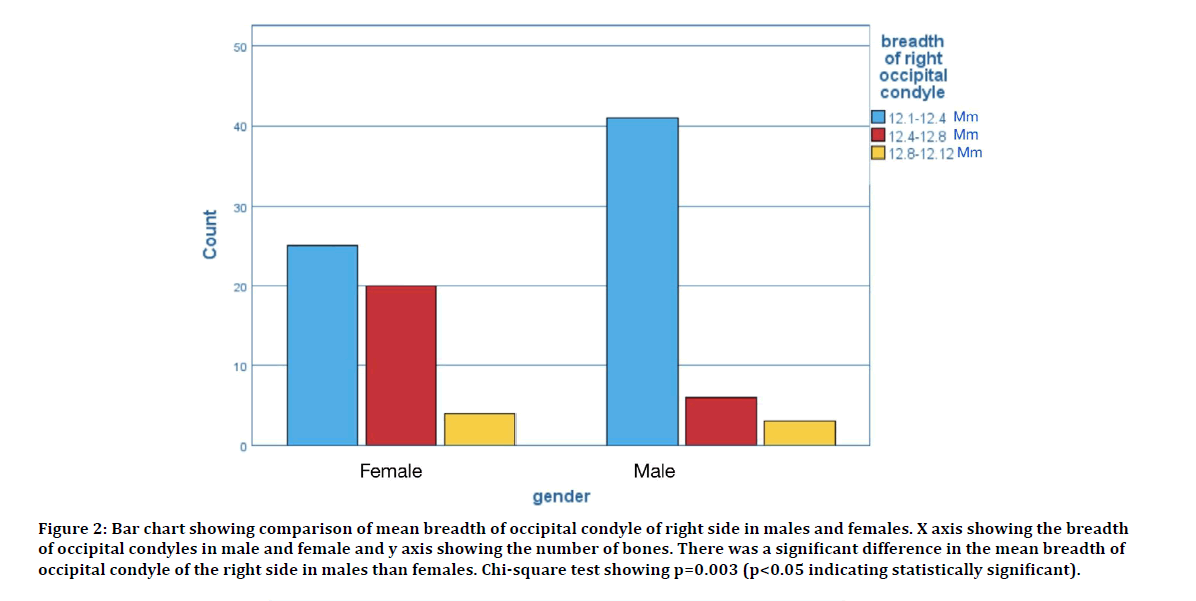
Figure 2: Bar chart showing comparison of mean breadth of occipital condyle of right side in males and females. X axis showing the breadth of occipital condyles in male and female and y axis showing the number of bones. There was a significant difference in the mean breadth of occipital condyle of the right side in males than females. Chi-square test showing p=0.003 (p<0.05 indicating statistically significant).
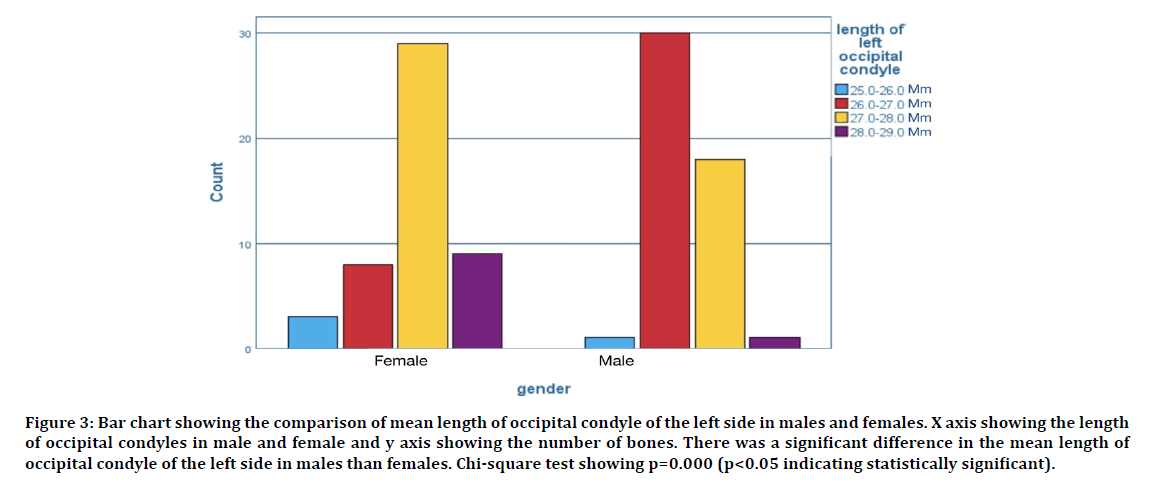
Figure 3: Bar chart showing the comparison of mean length of occipital condyle of the left side in males and females. X axis showing the length of occipital condyles in male and female and y axis showing the number of bones. There was a significant difference in the mean length of occipital condyle of the left side in males than females. Chi-square test showing p=0.000 (p<0.05 indicating statistically significant).
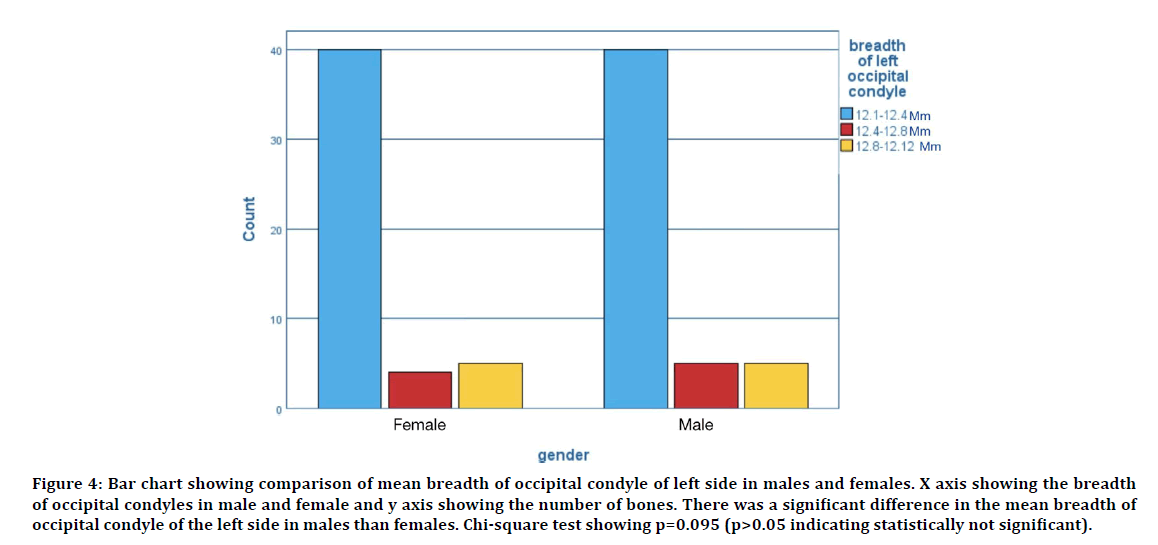
Figure 4: Bar chart showing comparison of mean breadth of occipital condyle of left side in males and females. X axis showing the breadth of occipital condyles in male and female and y axis showing the number of bones. There was a significant difference in the mean breadth of occipital condyle of the left side in males than females. Chi-square test showing p=0.095 (p>0.05 indicating statistically not significant).
The average length of the intercondylar distance in male was found to be 30.41 ± 4.75 mm. The average length of the intercondylar distance in females was found to be 27.76 ± 3.88 mm. The comparison of average length of intercondylar distance in male and female is shown in Figure 5. The average diameter of the foramen magnum in male was found to be 31.52 ± 5.14 mm. The average diameter of the foramen magnum in females was found to be 29.18 ± 4.32 mm. The comparison of average diameter of foramen magnum in male and female is shown in Figure 6.
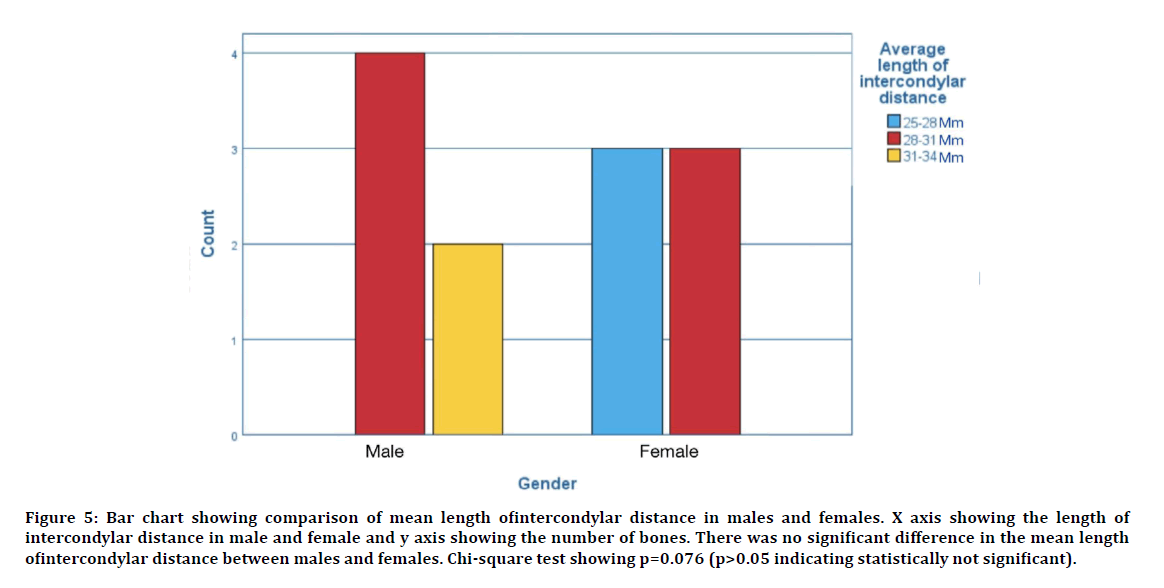
Figure 5: Bar chart showing comparison of mean length ofintercondylar distance in males and females. X axis showing the length of intercondylar distance in male and female and y axis showing the number of bones. There was no significant difference in the mean length ofintercondylar distance between males and females. Chi-square test showing p=0.076 (p>0.05 indicating statistically not significant).
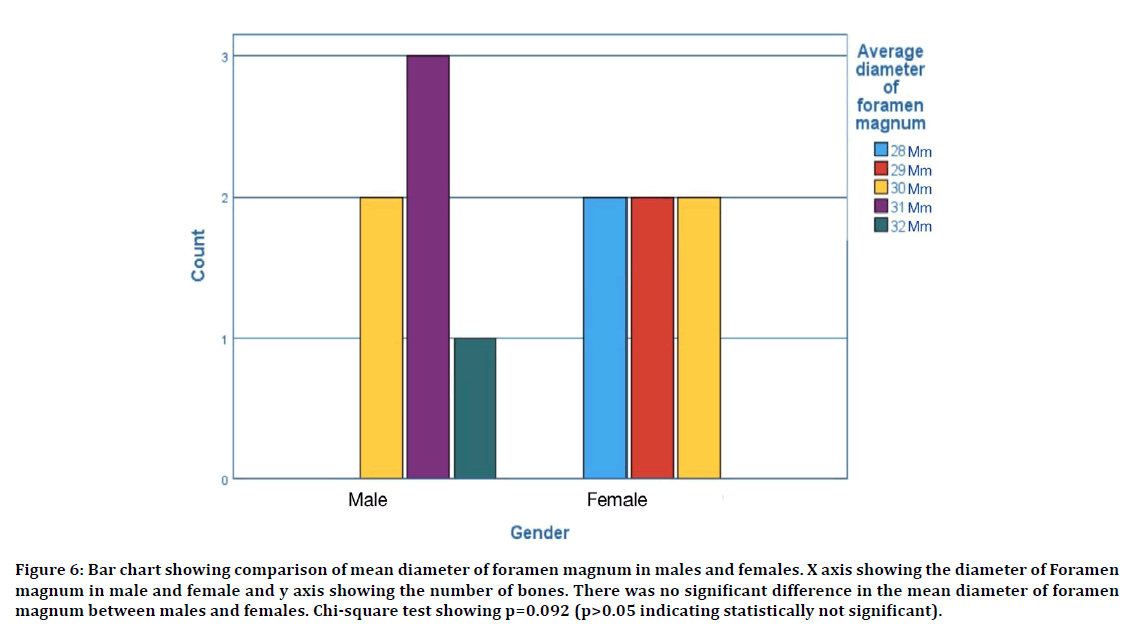
Figure 6: Bar chart showing comparison of mean diameter of foramen magnum in males and females. X axis showing the diameter of Foramen magnum in male and female and y axis showing the number of bones. There was no significant difference in the mean diameter of foramen magnum between males and females. Chi-square test showing p=0.092 (p>0.05 indicating statistically not significant).
Between the male and female skulls, statistically significant differences were found for the length and breadth of the occipital condyles of the right side in males than females (p<0.05). Also there was a statistically significant difference in the length and breadth of the occipital condyles of the left side in males than females (p<0.05).
Between the male and female skulls, statistically significant differences were found for the intercondylar distance between the males and females (p>0.05). Also there was no significant difference in the average diameter of the foramen magnum between the males and females (p>0.05).
Regression analysis studies have been performed for the morphology of Foramen magnum and Occipital condyle for identification of sex, ethnic group and age [23–25]. Although some studies suggested these did not have a correlation with the sagittal and the transverse diameter of the Foramen magnum [26,27] other studies reported a sexual dimorphism for Foramen magnum dimensions with [28,29] all parameters being significantly higher in males.
In our study, males displayed larger mean values than females regarding length of foramen magnum and width of foramen magnum. This is similar to the findings of Kamath et al. [29,30] found that sex predictability is higher values in males for Foramen magnum (70.3%), followed by sagittal diameter (69.6%), and least for transverse diameter (66.4%), similar to the study of Uthman et al. [31] for Foramen magnum area and Sagital diameter [32] with higher predictability for Foramen magnum and sagittal diameter compared to transverse diameter. Rai et al. [33] found that Occipital condyle and Foramen magnum dimensions were higher in males compared to females. No statistical significant difference was found in adults for different [34–36] age groups for the Occipital condyle and Foramen magnum Varsha et al. found that the antero-posterior diameter of the occipital condyle in male skulls was found higher than the female skulls, however there was no significant difference in the transverse diameter of Occipital condyle in male and female skulls. The results clearly indicate males displayed larger mean values than female’s length of Foramen magnum and width of Foramen magnum [37]. Some of the authors described that even discriminative formulae that are helpful to establish gender of the skull based on the morphology of the occipital bone or just its small part. The most common one is so-called Fisher’s method that calculates probability on the basis of occipital condyle length (OcL) and occipital condyle width (OcW) as well as width of the foramen magnum (FmW) using the following formula,
Diameter of male=[(8.227 x OcL)+(6.885 x OcW)+(5.817 x FmW)]-227.181
Diameter of female=[(7.529 x OcL)+(6.477 x OcW)+(5.467 x FmW)]-196.519
The method was successfully applied by Giles et al. [38] who were able to correctly state sex of Afro- Americans (82%) and Caucasian (89%) individuals. Similar accuracy was reported by Hanke et al. [39]. However, a much lower degree of proper determination of male (79.4%) and especially females (79.1%) was reported by Kajanoja et al. [40]. Gagandeep et al. reported that Maximum bicondylar breadth, length found to be a more discriminating variable providing accuracy 66% [41]. According to Gapert et al. sexual dimorphism expression is increased in occipital condyles compared to foramen magnum [42,43]. Zirahei et al. reported that Males presented higher mean values of 24.15 mm and 26.83 mm for anterior intercondylar distance and posterior intercondylar distance, respectively. While females are 22.31 mm and 23.79 mm [44]. Abdel-Karim et al., reported Anterior occipital inter condylar distance (AOID) mean values of 7.22 mm and 6.83 mm for males and females respectively, while the posterior occipital inter condylar distance (POID) mean values are 31.57 mm and 30.42 mm in a study [45]. Several studies confirm that sex determinationis significant using Occipital condyle, intercondylar distance, foramen magnum.
Thus the evidence adds to the consensus for this study and can be used as one of the reliable criteria for determination of sex. In this present study, limitations such as the exact age of the skull were not determined. This Study was done in a small sample size. With this we can conclude that the data obtained from the present study may be of use to the forensic expert’s neurosurgeons anthropologists morphologists clinical anatomists carrying out further research work.
Conclusion
The morphometric values of occipital condyles are variable. So the knowledge of these variations may guide neurosurgeons in transcondylar approach in the management of neoplasms and other pathology related to this region. The foramen magnum is of particular interest in the field of forensic medicine to identify fire victims and also used for intracranial surgical approaches. The result of this study offers a good opportunity to identify sex using the occipital condyle, intercondylar distance and foramen magnum apart from pelvimetric and craniometric analysis of sex determination. Detailed morphometric analysis of occipital condyle, intercondylar distance foramen magnum will help in the estimation of sex though all the parameters doesn’t prove to be effective but it can serve as an additional criteria in case of skull obtained with damages on the cranial bones in forensic investigation and related fields. This study will be useful also for the anatomist, neurosurgeon, radiologist and morphologists’ clinical anatomists to carry out further detailed morphometric analysis.
References
- Priya A. Morphometric study of occipital condyles in north indian skulls. Med Int J of Anatomy 2019; 7:6841–6846.
- Sekar D, Lakshmanan G, Mani P, et al. Methylation-dependent circulating microRNA 510 in preeclampsia patients. Hypertens Res 2019; 42:1647–1648.
- Johnson J, Lakshmanan G, Sekar D, et al. Computational identification of MiRNA-7110 from pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) ESTs: A new microRNA that links diabetes and PAH. Hypertens Res 2020; 43:360–362.
- Seppan P, Muhammed I, Mohanraj KG, et al. Therapeutic potential of Mucuna pruriens (Linn.) on ageing induced damage in dorsal nerve of the penis and its implication on erectile function: An experimental study using albino rats. Aging Male 2018; 13:1–14.
- Datta AK. Essentials of human anatomy: Thorax, abdomen and pelvis. Current Books International 2010; 418.
- Al-Mefty O, Borba LA, Aoki N, et al. The transcondylar approach to extradural nonneoplastic lesions of the craniovertebral junction. J Neurosurg 1996; 84:1–6.
- Ziyal IM. The surgical anatomy of six variations of the extreme lateral approach. J Neurosurg 1999; 9:105–112.
- Isaac Cheruiyot PM. Morphometry of occipital condyles: Implications for Transcondylar approach to craniovertebral junction lessons. Anat J Afr 2018; 7:1224–1231.
- Mahajan D. An anatomical perspective of human occipital condyles and foramen magnum with neurosurgical correlates. IJCDA 2013; 6:29–33.
- Krishna RN. Estimation of stature from psyiognomic facial length and morphological facial length. Res J Pharm and Tech 2016; 9:2071–2073.
- El-Gheriani AS. A new guide for positioning of maxillary posterior denture teeth. J Oral Rehabil 1992; 19:535–538.
- Nandhini, Taslima JS, Babu YS, et al. Size, shape, prominence and localization of gerdy's tubercle in dry human tibial bones. J Adv Pharm Technol Res 2018; 11:3604.
- Subashri, Thenmozhi MS. Occipital emissary foramina in human adults and their clinical implication. J Adv Pharm Technol Res. 2016; 9:716.
- Singh A. Morphological and morphometric study of foramen magnum in dry human skull and its clinical significance. Int J Anat Radiol Surg 2019; 8:AO10–22.
- Thejeswar EP, Thenmozhi MS. Educational research ipad system vs textbook system. J Adv Pharm Technol Res 2015; 8:1158.
- Sriram, Nirisha, Thenmozhi, et al. Effects of mobile phone radiation on the brain. Research J Pharm and Tech 2015; 8:867.
- Murshed KA. Morphometric evaluation of the foramen magnum and variations in its shape: A study on computerized tomographic images of normal adults. Turk J Med Sci 2003; 33:301–306.
- Keerthana B, Thenmozhi MS. Occurrence of foramen huschke and its clinical significance. Research J Pharm and Tech 2016; 9:1841–1842.
- Pratha AA, Thenmozhi MS. The study of occurrence and morphometric analysis of meningo orbital foramen. Research J Pharm Tech 2016; 9:880–882.
- Radhakrishna SK, Shivarma CH, Ramakrishna A. Morphometric analysis of foramen magnum for sex determination in south Indian population. NUJHS 2012; 2:20–22.
- Sampada PK. Morphometric and morphological study of foramen magnum in dried human skull bones. Int J of Anatomy 2017; 5:3682–3686.
- Menon A, Thenmozhi MS. Correlation between thyroid function and obesity. Research J Pharm and Tech 2016; 9: 1568–1570.
- Olivier G. Biometry of the human occipital bone. J Anat 1975; 120:507–518.
- Samuel AR, Thenmozhi MS, et al. Study of impaired vision due to Amblyopia. J Adv Pharm Technol Res 2015; 8:912–914.
- Hafeez N, Thenmozhi MS, et al. Accessory foramen in the middle cranial fossa. Research journal of pharmacy and technology 2016; 9:1880–1882.
- Gruber P, Henneberg M, Böni T, et al. Variability of human foramen magnum size. Anat Rec 2009; 292:1713–1719.
- Choudhari S, Thenmozhi MS. Occurrence and importance of posterior condylar foramen. J Adv Pharm Technol Res 2016; 9:1083–1085.
- Raikar N, Meundi M, David C, et al. Sexual dimorphism in foramen magnum dimensions in the South Indian population: A digital submentovertex radiographic study. Research J Pharm and Tech 2016; 8:180.
- Kamath VG, Asif M, Shetty R, et al. Binary logistic regression analysis of foramen magnum dimensions for sex determination. Int J Anat Res 2015; 15:1–9.
- Kannan R, Thenmozhi MS. Morphometric study of the styloid process and its clinical importance on eagles syndrome. J Adv Pharm Technol Res 2016; 9:1137.
- Uthman AT, Al-Rawi NH, Al-Timimi JF, et al. Evaluation of foramen magnum in gender determination using helical CT scanning. Dentomaxillofac Radiol 2012; 14:197–202.
- Raghavendra Babu YP, Kanchan T, Attiku Y, et al. Sex estimation from foramen magnum dimensions in an Indian population. J Forensic Leg Med 2012; 19:162–167.
- Rai H, Keluskar V, Patil S, et al. Accuracy of measurements of foramen magnum and occipital condyle as an indicator for sex determination using computed tomography. Indian J Med Res 2017;10: 80.
- Bello SM, sTadros AADZ. Measurements of occipital condyles using computerized tomography from sokoto state, Nigeria. Int J Healthc 2013; 2:10–17.
- Kanodia G, Parihar V, Yadav YR, et al. Morphometric analysis of posterior fossa and foramen magnum. J Neurosci Rural Pract 2012; 3:261–266.
- Sholapurkar VT. Morphometric analysis of human occipital condyles for sex determination in dry adult skulls. Int J Anat Radiol Surg 2017; 5:3318–3323.
- Sengul G. Morphological analysis of occipital condyles and foramen magnum as a guide for lateral surgical approaches. Anat Physiol 2017; 3.
- Giles E, Elliot O. Sex determination by discriminant function analysis of crania. Am J Phys Anthropol 1963; 21:53–68.
- Henke W. On the method of discriminant function analysis for sex determination of the skull. J Human Evol 1977; 6:95–100.
- Kajanoja P. Sex determination of finnish crania by discriminant function analysis. Int J of Anatomy 1966; 24:29–33.
- Gagandeep singh IT. Morphometric analysis of foramen magnum in human skull for sex determinaation. Hum Biol 2013; 2:29–41.
- Manoel CPFB. Morphometric analysis of the foramen magnum in human skulls of brazillizn individuals: Its relation to gender. J Morphol Sci 2009; 26:104–108.
- Gapert R, Black S, Last J, et al. Sex determination from the foramen magnum: discriminant function analysis in an eighteenth and nineteenth century British sample. Int J Legal Med 2009; 123:25–33.
- Zirahei JV. The effects of artesunate on the haematopoietic cells in wistar rats. J Appl Dent 2013; 11: 41–44.
- Abdel-Karim RI, Housseini AM, Hashish RK, et al. Adult sex estimation using three dimensional volume rendering multislice computed tomography of the foramen magnum and occipital condyles : A study in Egyptian population. Int J Adv Res 2015; 3:1212–1215.
Author Info
Aksha Sharen A and Karthik Ganesh Mohanraj*
Department of Anatomy, Saveetha Dental College, Saveetha Institute of Medical and Technical Sciences (SIMATS), Saveetha University, Chennai, IndiaCitation: Aksha Sharen A, Karthik Ganesh Mohanraj, Determination of Sex by Occipital Condyle Intercondylar Distance and Foramen Magnum Among South Indian Population, J Res Med Dent Sci, 2020, 8 (7): 227-233.
Received: 27-Sep-2020 Accepted: 27-Oct-2020 Published: 03-Nov-2020
